| 1 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
[](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32)
|
| 2 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 3 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
# The NEORV32 RISC-V Processor
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
43 |
zero_gravi |
[](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Processor+Check%22)
|
| 6 |
|
|
[](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22RISC-V+Compliance%22)
|
| 7 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
[](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/LICENSE)
|
| 8 |
|
|
[](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases)
|
| 9 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
* [Overview](#Overview)
|
| 11 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* [Status](#Status)
|
| 12 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* [Features](#Features)
|
| 13 |
|
|
* [FPGA Implementation Results](#FPGA-Implementation-Results)
|
| 14 |
|
|
* [Performance](#Performance)
|
| 15 |
30 |
zero_gravi |
* [Top Entities](#Top-Entities)
|
| 16 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* [**Getting Started**](#Getting-Started)
|
| 17 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* [Contribute/Feedback/Questions](#ContributeFeedbackQuestions)
|
| 18 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* [Legal](#Legal)
|
| 19 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
## Overview
|
| 23 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 24 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
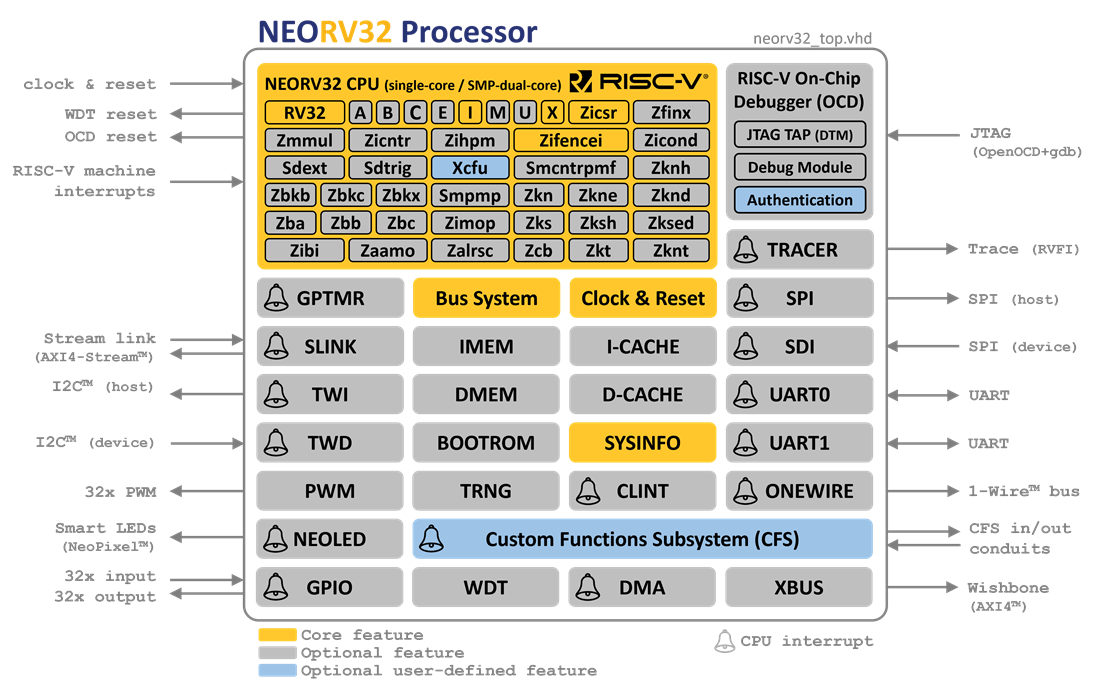
The NEORV32 Processor is a customizable microcontroller-like system on chip (SoC) that is based
|
| 25 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
on the RISC-V-compliant NEORV32 CPU. The processor is intended as *ready-to-go* auxiliary processor within a larger SoC
|
| 26 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
designs or as stand-alone custom microcontroller.
|
| 27 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 28 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
:books: For detailed information take a look at the [NEORV32 data sheet (pdf)](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
| 29 |
|
|
The doxygen-based documentation of the *software framework* is available online at [GitHub-pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html).
|
| 30 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 31 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
:label: The project’s change log is available as [CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) in the root directory of this repository.
|
| 32 |
|
|
To see the changes between *stable* releases visit the project's [release page](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases).
|
| 33 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 34 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
:spiral_notepad: Check out the [project boards](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/projects) for a list of current ideas, ToDos, features being planned and work being in-progress.
|
| 35 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 36 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
:bulb: Feel free to open a [new issue](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/issues) or start a [new discussion](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/discussions)
|
| 37 |
|
|
if you have questions, comments, ideas or bug-fixes. Check out how to [contribute](#ContributeFeedbackQuestions).
|
| 38 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 39 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 40 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
### Key Features
|
| 41 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 42 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
* RISC-V 32-bit `rv32` [**NEORV32 CPU**](#NEORV32-CPU-Features), compliant to
|
| 43 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* subset of the *Unprivileged ISA Specification* [(Version 2.2)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)
|
| 44 |
|
|
* subset of the *Privileged Architecture Specification* [(Version 1.12-draft)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-privileged.pdf)
|
| 45 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
* the [official RISC-V compliance tests](#Status) (*passing*)
|
| 46 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
* Configurable RISC-V-compliant CPU extensions
|
| 47 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* [`A`](#A---Atomic-memory-access-extension) - atomic memory access instructions (optional)
|
| 48 |
|
|
* [`B`](#B---Bit-manipulation-instructions-extension) - Bit manipulation instructions (optional)
|
| 49 |
|
|
* [`C`](#C---Compressed-instructions-extension) - compressed instructions (16-bit) (optional)
|
| 50 |
|
|
* [`E`](#E---Embedded-CPU-version-extension) - embedded CPU (reduced register file size) (optional)
|
| 51 |
|
|
* [`I`](#I---Base-integer-instruction-set) - base integer instruction set (always enabled)
|
| 52 |
|
|
* [`M`](#M---Integer-multiplication-and-division-hardware-extension) - integer multiplication and division hardware (optional)
|
| 53 |
|
|
* [`U`](#U---Privileged-architecture---User-mode-extension) - less-privileged *user mode* (optional)
|
| 54 |
|
|
* [`X`](#X---NEORV32-specific-CPU-extensions) - NEORV32-specific extensions (always enabled)
|
| 55 |
|
|
* [`Zicsr`](#Zicsr---Privileged-architecture---CSR-access-extension) - control and status register access instructions (+ exception/irq system) (optional)
|
| 56 |
|
|
* [`Zifencei`](#Zifencei---Privileged-architecture---Instruction-stream-synchronization-extension) - instruction stream synchronization (optional)
|
| 57 |
|
|
* [`PMP`](#PMP---Privileged-architecture---Physical-memory-protection) - physical memory protection (optional)
|
| 58 |
|
|
* [`HPM`](#HPM---Privileged-architecture---Hardware-performance-monitors) - hardware performance monitors (optional)
|
| 59 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
* Full-scale RISC-V microcontroller system / **SoC** [**NEORV32 Processor**](#NEORV32-Processor-Features) with optional submodules
|
| 60 |
41 |
zero_gravi |
* optional embedded memories (instructions/data/bootloader, RAM/ROM) and caches
|
| 61 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* timers (watch dog, RISC-V-compliant machine timer)
|
| 62 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
* serial interfaces (SPI, TWI, UARTs)
|
| 63 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* general purpose IO and PWM channels
|
| 64 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* external bus interface (Wishbone / [AXI4](#AXI4-Connectivity))
|
| 65 |
48 |
zero_gravi |
* subsystem for custom co-processors
|
| 66 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* [more ...](#NEORV32-Processor-Features)
|
| 67 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
* Software framework
|
| 68 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* core libraries for high-level usage of the provided functions and peripherals
|
| 69 |
|
|
* application compilation based on [GNU makefiles](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/blink_led/makefile)
|
| 70 |
46 |
zero_gravi |
* GCC-based toolchain ([pre-compiled toolchains available](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt))
|
| 71 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
* bootloader with UART interface console
|
| 72 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
* runtime environment
|
| 73 |
|
|
* several example programs
|
| 74 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
* [doxygen-based](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/doxygen_makefile_sw) software documentation: available on [GitHub pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html)
|
| 75 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
* [FreeRTOS port](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/demo_freeRTOS) available
|
| 76 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
* [**Full-blown data sheet**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf)
|
| 77 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
* Completely described in behavioral, platform-independent VHDL - no primitives, macros, etc.
|
| 78 |
|
|
* Fully synchronous design, no latches, no gated clocks
|
| 79 |
|
|
* Small hardware footprint and high operating frequency
|
| 80 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 81 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 82 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
### Design Principles
|
| 83 |
|
|
|
| 84 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
* From zero to *hello_world*: Completely open source and documented.
|
| 85 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Plain VHDL without technology-specific parts like attributes, macros or primitives.
|
| 86 |
|
|
* Easy to use – working out of the box.
|
| 87 |
|
|
* Clean synchronous design, no wacky combinatorial interfaces.
|
| 88 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Be as small as possible – but with a reasonable size-performance trade-off.
|
| 89 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* Be as RISC-V-compliant as possible.
|
| 90 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* The processor has to fit in a Lattice iCE40 UltraPlus 5k low-power FPGA running at 22+ MHz.
|
| 91 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 92 |
|
|
|
| 93 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
### Status
|
| 94 |
3 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 95 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
The processor is [synthesizable](#FPGA-Implementation-Results) (tested on *real hardware* using Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx Vivado and Lattice Radiant/Synplify Pro) and can successfully execute
|
| 96 |
30 |
zero_gravi |
all the [provided example programs](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example) including the [CoreMark benchmark](#CoreMark-Benchmark).
|
| 97 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 98 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
**RISC-V Compliance**: The processor passes the official `rv32_m/C`, `rv32_m/I`, `rv32_m/M`, `rv32_m/privilege` and `rv32_m/Zifencei`
|
| 99 |
|
|
[RISC-V compliance](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-compliance) tests. More information regarding the NEORV32 port of the compliance framework can be found in
|
| 100 |
|
|
[`riscv-compliance/README.md`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/riscv-compliance/README.md).
|
| 101 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 102 |
43 |
zero_gravi |
| Project component | CI status |
|
| 103 |
|
|
|:----------------- |:----------|
|
| 104 |
|
|
| [NEORV32 processor](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Processor+Check%22) |
|
| 105 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
| [SW Framework Documentation (online @GH-pages)](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) | [](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) |
|
| 106 |
46 |
zero_gravi |
| [Pre-built toolchains](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Test+Toolchains%22) |
|
| 107 |
43 |
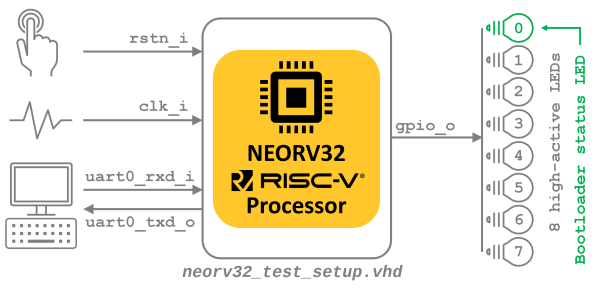
zero_gravi |
| [RISC-V compliance test](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/riscv-compliance/README.md) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22RISC-V+Compliance%22) |
|
| 108 |
6 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 109 |
|
|
|
| 110 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
## Features
|
| 111 |
|
|
|
| 112 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
The full-blown data sheet of the NEORV32 Processor and CPU is available as pdf file:
|
| 113 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
| 114 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 115 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 116 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
### NEORV32 Processor Features
|
| 117 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 118 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 119 |
|
|
|
| 120 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
The NEORV32 Processor provides a full-scale microcontroller-like SoC based on the NEORV32 CPU. The setup
|
| 121 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
is highly customizable via the processor's top generics and already provides the following *optional* modules:
|
| 122 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 123 |
41 |
zero_gravi |
* processor-internal data and instruction memories (**DMEM** / **IMEM**) & cache (**iCACHE**)
|
| 124 |
|
|
* bootloader (**BOOTLDROM**) with UART console and automatic application boot from SPI flash option
|
| 125 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* machine system timer (**MTIME**), RISC-V-compliant
|
| 126 |
|
|
* watchdog timer (**WDT**)
|
| 127 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* two independent universal asynchronous receivers and transmitters (**UART0** & **UART1**) with optional hardware flow control (RTS/CTS)
|
| 128 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* 8/16/24/32-bit serial peripheral interface controller (**SPI**) with 8 dedicated chip select lines
|
| 129 |
|
|
* two wire serial interface controller (**TWI**), with optional clock-stretching, compatible to the I²C standard
|
| 130 |
|
|
* general purpose parallel IO port (**GPIO**), 32xOut & 32xIn, with pin-change interrupt
|
| 131 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* 32-bit external bus interface, Wishbone b4 compliant (**WISHBONE**)
|
| 132 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
* wrapper for **AXI4-Lite Master Interface** (see [AXI Connectivity](#AXI4-Connectivity))
|
| 133 |
|
|
* PWM controller with 4 channels and 8-bit duty cycle resolution (**PWM**)
|
| 134 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* ring-oscillator-based true random number generator (**TRNG**)
|
| 135 |
|
|
* custom functions subsystem (**CFS**) for tightly-coupled custom co-processor extensions
|
| 136 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
* numerically-controlled oscillator (**NCO**) with three independent channels
|
| 137 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* system configuration information memory to check hardware configuration by software (**SYSINFO**)
|
| 138 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 139 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 140 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
### NEORV32 CPU Features
|
| 141 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 142 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
The NEORV32 CPU is **compliant** to the
|
| 143 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
[official RISC-V specifications (2.2)](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf) including a subset of the
|
| 144 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
[RISC-V privileged architecture specifications (1.12-draft)](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)
|
| 145 |
|
|
tested via the [official RISC-V Compliance Test Framework](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-compliance)
|
| 146 |
|
|
(see [`riscv-compliance/README`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/riscv-compliance/README.md)).
|
| 147 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 148 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
More information regarding the CPU including a detailed list of the instruction set and the available CSRs can be found in
|
| 149 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
the [:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
| 150 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 151 |
|
|
|
| 152 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
#### General Features
|
| 153 |
|
|
|
| 154 |
26 |
zero_gravi |
* Modified Harvard architecture (separate CPU interfaces for data and instructions; NEORV32 processor: Single processor-internal bus via I/D mux)
|
| 155 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
* Two stages in-order pipeline (FETCH, EXECUTE); each stage uses a multi-cycle processing scheme
|
| 156 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
* No hardware support of unaligned accesses - they will trigger an exception
|
| 157 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* BIG-ENDIAN byte-order, processor's external memory interface allows endianness configuration to connect to system with different endianness
|
| 158 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
* All reserved or unimplemented instructions will raise an illegal instruction exception
|
| 159 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
* Privilege levels: `machine` mode, `user` mode (if enabled via `U` extension)
|
| 160 |
33 |
zero_gravi |
* Official [RISC-V open-source architecture ID](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md)
|
| 161 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 162 |
|
|
|
| 163 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `A` - Atomic memory access extension
|
| 164 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 165 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* Supported instructions: `LR.W` (load-reservate) `SC.W` (store-conditional)
|
| 166 |
|
|
|
| 167 |
|
|
|
| 168 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `B` - Bit manipulation instructions extension
|
| 169 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 170 |
|
|
* :warning: Extension is not officially ratified yet by the RISC-V foundation!
|
| 171 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Implies `Zbb` & `Zbs` sub-extensions (the remaining `B` sub-extensions are not supported yet)
|
| 172 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* Compatible to [v0.94-draft](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/bitmanip-draft.pdf) of the bit manipulation spec
|
| 173 |
|
|
* Support via intrisc library (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation))
|
| 174 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* `Zbb` Base instruction set: `CLZ` `CTZ` `CPOP` `SEXT.B` `SEXT.H` `MIN[U]` `MAX[U]` `ANDN` `ORN` `XNOR` `ROL` `ROR[I]` `zext`(*pseudo-instruction* for `PACK rd, rs, zero`) `rev8`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GREVI rd, rs, -8`) `orc.b`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GORCI rd, rs, 7`)
|
| 175 |
|
|
* `Zbs` Single-bit instructions: `SBSET[I]` `SBCLR[I]` `SBINV[I]` `SBEXT[I]`
|
| 176 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 177 |
|
|
|
| 178 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `C` - Compressed instructions extension
|
| 179 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 180 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* ALU instructions: `C.ADDI4SPN` `C.ADD[I]` `C.ADDI16SP` `C.LI` `C.LUI` `C.SLLI` `C.SRLI` `C.SRAI` `C.ANDI` `C.SUB` `C.XOR` `C.OR` `C.AND` `C.MV` `C.NOP`
|
| 181 |
7 |
zero_gravi |
* Jump and branch instructions: `C.J` `C.JAL` `C.JR` `C.JALR` `C.BEQZ` `C.BNEZ`
|
| 182 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Memory instructions: `C.LW` `C.SW` `C.LWSP` `C.SWSP`
|
| 183 |
25 |
zero_gravi |
* System instructions: `C.EBREAK` (only with `Zicsr` extension)
|
| 184 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
| 185 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 186 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `E` - Embedded CPU version extension
|
| 187 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 188 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Reduced register file (only the 16 lowest registers)
|
| 189 |
|
|
|
| 190 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 191 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `I` - Base integer instruction set
|
| 192 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 193 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* ALU instructions: `LUI` `AUIPC` `ADD[I]` `SLT[I][U]` `XOR[I]` `OR[I]` `AND[I]` `SLL[I]` `SRL[I]` `SRA[I]` `SUB`
|
| 194 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* Jump and branch instructions: `JAL` `JALR` `BEQ` `BNE` `BLT` `BGE` `BLTU` `BGEU`
|
| 195 |
|
|
* Memory instructions: `LB` `LH` `LW` `LBU` `LHU` `SB` `SH` `SW`
|
| 196 |
|
|
* System instructions: `ECALL` `EBREAK` `FENCE`
|
| 197 |
|
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
| 198 |
|
|
|
| 199 |
|
|
|
| 200 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `M` - Integer multiplication and division hardware extension
|
| 201 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 202 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Multiplication instructions: `MUL` `MULH` `MULHSU` `MULHU`
|
| 203 |
|
|
* Division instructions: `DIV` `DIVU` `REM` `REMU`
|
| 204 |
19 |
zero_gravi |
* By default, the multiplier and divider cores use an iterative bit-serial processing scheme
|
| 205 |
|
|
* Multiplications can be mapped to DSPs via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic to increase performance
|
| 206 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 207 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 208 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `U` - Privileged architecture - User mode extension
|
| 209 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 210 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
| 211 |
|
|
* Privilege levels: `M` (machine mode) + less-privileged `U` (user mode)
|
| 212 |
|
|
|
| 213 |
|
|
|
| 214 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `X` - NEORV32-specific CPU extensions
|
| 215 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 216 |
|
|
* The NEORV32-specific extensions are always enabled and are indicated via the `X` bit set in the `misa` CSR.
|
| 217 |
48 |
zero_gravi |
* 16 *fast interrupt* request channels with according control/status bits in `mie` and `mip` and custom exception codes in `mcause`
|
| 218 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
* `mzext` CSR to check for implemented `Z*` CPU extensions (like `Zifencei`)
|
| 219 |
|
|
* All undefined/umimplemented/malformed/illegal instructions do raise an illegal instruction exception
|
| 220 |
|
|
|
| 221 |
|
|
|
| 222 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `Zicsr` - Privileged architecture - CSR access extension
|
| 223 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 224 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Privilege levels: `M-mode` (Machine mode)
|
| 225 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* CSR access instructions: `CSRRW[I]` `CSRRS[I]` `CSRRC[I]`
|
| 226 |
8 |
zero_gravi |
* System instructions: `MRET` `WFI`
|
| 227 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
| 228 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
* Counter CSRs: `[m]cycle[h]` `[m]instret[m]` `time[h]` `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31, configurable) `mcounteren` `mcountinhibit` `mhpmevent*`(3..31, configurable)
|
| 229 |
|
|
* Machine CSRs: `mstatus[h]` `misa`(read-only!) `mie` `mtvec` `mscratch` `mepc` `mcause` `mtval` `mip` `mvendorid` [`marchid`](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md) `mimpid` `mhartid` `mzext`(custom)
|
| 230 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Supported (sync.) exceptions (all RISC-V-compliant):
|
| 231 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Misaligned instruction address
|
| 232 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Instruction access fault (via timeout/error after unacknowledged bus access)
|
| 233 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Illegal instruction
|
| 234 |
4 |
zero_gravi |
* Breakpoint (via `ebreak` instruction)
|
| 235 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
* Load address misaligned
|
| 236 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Load access fault (via timeout/error after unacknowledged bus access)
|
| 237 |
4 |
zero_gravi |
* Store address misaligned
|
| 238 |
38 |
zero_gravi |
* Store access fault (via unacknowledged bus access after timeout)
|
| 239 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* Environment call from U-mode (via `ecall` instruction in user mode)
|
| 240 |
|
|
* Environment call from M-mode (via `ecall` instruction in machine mode)
|
| 241 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* Supported (async.) exceptions / interrupts:
|
| 242 |
|
|
* Machine timer interrupt `mti` (via processor's MTIME unit / external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
| 243 |
|
|
* Machine software interrupt `msi` (via external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
| 244 |
|
|
* Machine external interrupt `mei` (via external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
| 245 |
|
|
* 16 fast interrupt requests (custom extension), 6+1 available for custom usage
|
| 246 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 247 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 248 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `Zifencei` - Privileged architecture - Instruction stream synchronization extension
|
| 249 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 250 |
41 |
zero_gravi |
* System instructions: `FENCE.I` (among others, used to clear and reload instruction cache)
|
| 251 |
8 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 252 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 253 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `PMP` - Privileged architecture - Physical memory protection
|
| 254 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 255 |
|
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
| 256 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
* Configurable number of regions (0..63)
|
| 257 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
* Additional machine CSRs: `pmpcfg*`(0..15) `pmpaddr*`(0..63)
|
| 258 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 259 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 260 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
#### `HPM` - Privileged architecture - Hardware performance monitors
|
| 261 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 262 |
|
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
| 263 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
* Configurable number of counters (0..29)
|
| 264 |
|
|
* Additional machine CSRs: `mhpmevent*`(3..31) `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31)
|
| 265 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 266 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 267 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
### :warning: Non-RISC-V-Compliant Issues and Limitations
|
| 268 |
|
|
|
| 269 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* CPU and Processor are BIG-ENDIAN, but this should be no problem as the external memory bus interface provides big- and little-endian configurations
|
| 270 |
30 |
zero_gravi |
* `misa` CSR is read-only - no dynamic enabling/disabling of synthesized CPU extensions during runtime; for compatibility: write accesses (in m-mode) are ignored and do not cause an exception
|
| 271 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
* The physical memory protection (**PMP**) only supports `NAPOT` mode yet and a minimal granularity of 8 bytes
|
| 272 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
* The `A` extension only implements `lr.w` and `sc.w` instructions yet. However, these instructions are sufficient to emulate all further AMO operations
|
| 273 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
* The `mcause` trap code `0x80000000` (originally reserved in the RISC-V specs) is used to indicate a hardware reset (as "non-maskable interrupt")
|
| 274 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
* The bit manipulation extension is not yet officially ratified, but is expected to stay unchanged. There is no software support in the upstream GCC RISC-V port yet. However, an intrinsic library is provided to utilize the provided bit manipulation extension from C-language code (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation)). NEORV32's `B` extension is compliant to spec. version "0.94-draft".
|
| 275 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 276 |
|
|
|
| 277 |
|
|
|
| 278 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
## FPGA Implementation Results
|
| 279 |
|
|
|
| 280 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
### NEORV32 CPU
|
| 281 |
|
|
|
| 282 |
|
|
This chapter shows exemplary implementation results of the NEORV32 CPU for an **Intel Cyclone IV EP4CE22F17C6N FPGA** on
|
| 283 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
a DE0-nano board. The design was synthesized using **Intel Quartus Prime Lite 20.1** ("balanced implementation"). The timing
|
| 284 |
4 |
zero_gravi |
information is derived from the Timing Analyzer / Slow 1200mV 0C Model. If not otherwise specified, the default configuration
|
| 285 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
of the CPU's generics is assumed (e.g. no physical memory protection, no hardware performance monitors).
|
| 286 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
No constraints were used at all.
|
| 287 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 288 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
Results generated for hardware version [`1.5.1.4`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
|
| 289 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 290 |
44 |
zero_gravi |
| CPU Configuration | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs | f_max |
|
| 291 |
|
|
|:-----------------------------------------|:----------:|:--------:|:-----------:|:----:|:-------:|
|
| 292 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
| `rv32i` | 979 | 409 | 1024 | 0 | 123 MHz |
|
| 293 |
|
|
| `rv32i` + `Zicsr` | 1789 | 847 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 294 |
|
|
| `rv32im` + `Zicsr` | 2381 | 1125 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 295 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `Zicsr` | 2608 | 1140 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 296 |
|
|
| `rv32imac` + `Zicsr` | 2621 | 1144 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 297 |
|
|
| `rv32imacb` + `Zicsr` | 3013 | 1310 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 298 |
|
|
| `rv32imacb` + `Zicsr` + `u` | 3031 | 1313 | 1024 | 0 | 122 MHz |
|
| 299 |
|
|
| `rv32imacb` + `Zicsr` + `u` + `Zifencei` | 3050 | 1313 | 1024 | 0 | 116 MHz |
|
| 300 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 301 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
Setups with enabled "embedded CPU extension" `E` show the same LUT and FF utilization and identical f_max as the according `I` configuration.
|
| 302 |
|
|
However, the size of the register file is cut in half.
|
| 303 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 304 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 305 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
### NEORV32 Processor-Internal Peripherals and Memories
|
| 306 |
|
|
|
| 307 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
Results generated for hardware version [`1.5.1.4`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
|
| 308 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 309 |
25 |
zero_gravi |
| Module | Description | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs |
|
| 310 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
|:----------|:-----------------------------------------------------|----:|----:|------------:|-----:|
|
| 311 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
| BOOT ROM | Bootloader ROM (default 4kB) | 3 | 1 | 32 768 | 0 |
|
| 312 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
| BUSSWITCH | Bus mux for CPU instr. & data interfaces | 65 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 313 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
| i-CACHE | Proc.-int. nstruction cache (default 1x4x64 bytes) | 234 | 156 | 8 192 | 0 |
|
| 314 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
| CFS | Custom functions subsystem | - | - | - | - |
|
| 315 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
| DMEM | Processor-internal data memory (default 8kB) | 6 | 2 | 65 536 | 0 |
|
| 316 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| GPIO | General purpose input/output ports | 67 | 65 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 317 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
| IMEM | Processor-internal instruction memory (default 16kb) | 6 | 2 | 131 072 | 0 |
|
| 318 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| MTIME | Machine system timer | 274 | 166 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 319 |
49 |
zero_gravi |
| NCO | Numerically-controlled oscillator | 254 | 226 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 320 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
| PWM | Pulse-width modulation controller | 71 | 69 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 321 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| SPI | Serial peripheral interface | 138 | 124 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 322 |
|
|
| SYSINFO | System configuration information memory | 11 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 323 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
| TRNG | True random number generator | 132 | 105 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 324 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| TWI | Two-wire interface | 77 | 46 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 325 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
| UART0/1 | Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter 0/1 | 176 | 132 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 326 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| WDT | Watchdog timer | 60 | 45 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 327 |
39 |
zero_gravi |
| WISHBONE | External memory interface | 129 | 104 | 0 | 0 |
|
| 328 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 329 |
|
|
|
| 330 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
### NEORV32 Processor - Exemplary FPGA Setups
|
| 331 |
6 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 332 |
47 |
zero_gravi |
Exemplary processor implementation results for different FPGA platforms. The processor setup uses *the default peripheral configuration* (like no _CFS_ and no _TRNG_),
|
| 333 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
no external memory interface and only internal instruction and data memories. IMEM uses 16kB and DMEM uses 8kB memory space. The setup's top entity connects most of the
|
| 334 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
processor's [top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) signals
|
| 335 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
to FPGA pins - except for the Wishbone bus and the interrupt signals. The "default" strategy of each toolchain is used.
|
| 336 |
6 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 337 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
Results generated for hardware version [`1.4.9.0`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
|
| 338 |
6 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 339 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
| Vendor | FPGA | Board | Toolchain | CPU Configuration | LUT / LE | FF / REG | DSP | Memory Bits | BRAM / EBR | SPRAM | Frequency |
|
| 340 |
|
|
|:--------|:----------------------------------|:-----------------|:---------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------|:-----------|:-----------|:-------|:-------------|:-----------|:---------|--------------:|
|
| 341 |
|
|
| Intel | Cyclone IV `EP4CE22F17C6N` | Terasic DE0-Nano | Quartus Prime Lite 20.1 | `rv32imc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 3813 (17%) | 1904 (8%) | 0 (0%) | 231424 (38%) | - | - | 119 MHz |
|
| 342 |
|
|
| Lattice | iCE40 UltraPlus `iCE40UP5K-SG48I` | Upduino v2.0 | Radiant 2.1 (Synplify Pro) | `rv32ic` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 4397 (83%) | 1679 (31%) | 0 (0%) | - | 12 (40%) | 4 (100%) | *c* 22.15 MHz |
|
| 343 |
|
|
| Xilinx | Artix-7 `XC7A35TICSG324-1L` | Arty A7-35T | Vivado 2019.2 | `rv32imc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` + `PMP` | 2465 (12%) | 1912 (5%) | 0 (0%) | - | 8 (16%) | - | *c* 100 MHz |
|
| 344 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 345 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
**_Notes_**
|
| 346 |
20 |
zero_gravi |
* The Lattice iCE40 UltraPlus setup uses the FPGA's SPRAM memory primitives for the internal IMEM and DMEM (each 64kb).
|
| 347 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
The FPGA-specific memory components can be found in [`rtl/fpga_specific`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/fpga_specific/lattice_ice40up).
|
| 348 |
|
|
* The clock frequencies marked with a "c" are constrained clocks. The remaining ones are _f_max_ results from the place and route timing reports.
|
| 349 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
* The Upduino and the Arty board have on-board SPI flash memories for storing the FPGA configuration. These device can also be used by the default NEORV32
|
| 350 |
|
|
bootloader to store and automatically boot an application program after reset (both tested successfully).
|
| 351 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
* The setups with `PMP` implement 2 regions with a minimal granularity of 64kB.
|
| 352 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
* No HPM counters are implemented.
|
| 353 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 354 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 355 |
|
|
|
| 356 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
## Performance
|
| 357 |
|
|
|
| 358 |
|
|
### CoreMark Benchmark
|
| 359 |
|
|
|
| 360 |
|
|
The [CoreMark CPU benchmark](https://www.eembc.org/coremark) was executed on the NEORV32 and is available in the
|
| 361 |
|
|
[sw/example/coremark](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/coremark) project folder. This benchmark
|
| 362 |
|
|
tests the capabilities of a CPU itself rather than the functions provided by the whole system / SoC.
|
| 363 |
|
|
|
| 364 |
|
|
~~~
|
| 365 |
|
|
**Configuration**
|
| 366 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
Hardware: 32kB IMEM, 16kB DMEM, no caches, 100MHz clock
|
| 367 |
38 |
zero_gravi |
CoreMark: 2000 iterations, MEM_METHOD is MEM_STACK
|
| 368 |
|
|
Compiler: RISCV32-GCC 10.1.0 (rv32i toolchain)
|
| 369 |
|
|
Compiler flags: default, see makefile
|
| 370 |
|
|
Peripherals: UART for printing the results
|
| 371 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
~~~
|
| 372 |
|
|
|
| 373 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
Results generated for hardware version [`1.4.9.8`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
|
| 374 |
|
|
|
| 375 |
|
|
| CPU (including `Zicsr`) | Executable Size | Optimization | CoreMark Score | CoreMarks/MHz |
|
| 376 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
|:--------------------------------------------|:---------------:|:------------:|:--------------:|:-------------:|
|
| 377 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
| `rv32i` | 28 756 bytes | `-O3` | 36.36 | **0.3636** |
|
| 378 |
|
|
| `rv32im` | 27 516 bytes | `-O3` | 68.97 | **0.6897** |
|
| 379 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` | 22 008 bytes | `-O3` | 68.97 | **0.6897** |
|
| 380 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 22 008 bytes | `-O3` | 86.96 | **0.8696** |
|
| 381 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` + `FAST_SHIFT_EN` | 22 008 bytes | `-O3` | 90.91 | **0.9091** |
|
| 382 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 383 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic). The `FAST_SHIFT_EN` configuration
|
| 384 |
|
|
uses a barrel shifter for CPU shift operations (enabled via the `FAST_SHIFT_EN` generic).
|
| 385 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 386 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
When the `C` extension is enabled, branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
| 387 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 388 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 389 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
### Instruction Cycles
|
| 390 |
|
|
|
| 391 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
The NEORV32 CPU is based on a two-stages pipelined architecutre. Each stage uses a multi-cycle processing scheme. Hence,
|
| 392 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
each instruction requires several clock cycles to execute (2 cycles for ALU operations, ..., 40 cycles for divisions).
|
| 393 |
|
|
The average CPI (cycles per instruction) depends on the instruction mix of a specific applications and also on the available
|
| 394 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
CPU extensions. *By default* the CPU-internal shifter (e.g. for the `SLL` instruction) as well as the multiplier and divider of the
|
| 395 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
`M` extension use a bit-serial approach and require several cycles for completion.
|
| 396 |
|
|
|
| 397 |
6 |
zero_gravi |
The following table shows the performance results for successfully running 2000 CoreMark
|
| 398 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
iterations, which reflects a pretty good "real-life" work load. The average CPI is computed by
|
| 399 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
dividing the total number of required clock cycles (only the timed core to avoid distortion due to IO wait cycles; sampled via the `cycle[h]` CSRs)
|
| 400 |
19 |
zero_gravi |
by the number of executed instructions (`instret[h]` CSRs). The executables were generated using optimization `-O3`.
|
| 401 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 402 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
Results generated for hardware version [`1.4.9.8`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md).
|
| 403 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 404 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
| CPU (including `Zicsr`) | Required Clock Cycles | Executed Instructions | Average CPI |
|
| 405 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
|:--------------------------------------------|----------------------:|----------------------:|:-----------:|
|
| 406 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
| `rv32i` | 5 595 750 503 | 1 466 028 607 | **3.82** |
|
| 407 |
|
|
| `rv32im` | 2 966 086 503 | 598 651 143 | **4.95** |
|
| 408 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` | 2 981 786 734 | 611 814 918 | **4.87** |
|
| 409 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 2 399 234 734 | 611 814 918 | **3.92** |
|
| 410 |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` + `FAST_SHIFT_EN` | 2 265 135 174 | 611 814 948 | **3.70** |
|
| 411 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 412 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic). The `FAST_SHIFT_EN` configuration
|
| 413 |
|
|
uses a barrel shifter for CPU shift operations (enabled via the `FAST_SHIFT_EN` generic).
|
| 414 |
|
|
|
| 415 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
When the `C` extension is enabled branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
| 416 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 417 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 418 |
31 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 419 |
14 |
zero_gravi |
## Top Entities
|
| 420 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 421 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
The top entity of the **NEORV32 Processor** (SoC) is [`rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd),
|
| 422 |
|
|
which provides a Wishbone b4-compatoible bus interface.
|
| 423 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 424 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
:information_source: It is recommended to use the processor setup even if you want to **use the CPU in stand-alone mode**. Simply disable all the processor-internal
|
| 425 |
|
|
modules via the generics and you will get a "CPU wrapper" that already provides a minimal CPU environment and an external memory interface (like AXI4).
|
| 426 |
|
|
This setup also allows to further use the default bootloader and software framework. From this base you can start building your own processor system.
|
| 427 |
14 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 428 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
Use the top's generics to configure the system according to your needs. Each generic is initilized with the default configuration.
|
| 429 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
Detailed information regarding the interface signals and configuration generics can be found in
|
| 430 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
the [:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf).
|
| 431 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 432 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
All signals of the top entity are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively
|
| 433 |
|
|
(except for the processor's TWI signals, which are of type *std_logic*). Leave all unused output ports unconnected and tie all unused
|
| 434 |
|
|
input ports to zero.
|
| 435 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 436 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
**Alternative top entities**, like the simplified ["hello world" test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project) or CPU/Processor
|
| 437 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
wrappers with resolved port signal types (i.e. *std_logic*), can be found in [`rtl/top_templates`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates).
|
| 438 |
|
|
|
| 439 |
|
|
|
| 440 |
35 |
zero_gravi |
### AXI4 Connectivity
|
| 441 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 442 |
35 |
zero_gravi |
Via the [`rtl/top_templates/neorv32_top_axi4lite.vhd`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates/neorv32_top_axi4lite.vhd)
|
| 443 |
|
|
wrapper the NEORV32 provides an **AXI4-Lite** compatible master interface. This wrapper instantiates the default
|
| 444 |
|
|
[NEORV32 processor top entitiy](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) and implements a Wishbone to AXI4-Lite bridge.
|
| 445 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 446 |
35 |
zero_gravi |
The AXI4-Lite interface has been tested using Xilinx Vivado 19.2 block designer:
|
| 447 |
|
|
|
| 448 |
|
|

|
| 449 |
|
|
|
| 450 |
|
|
The processor was packed as custom IP using `neorv32_top_axi4lite.vhd` as top entity. The AXI interface is automatically detected by the packager.
|
| 451 |
|
|
All remaining IO interfaces are available as custom signals. The configuration generics are available via the "customize IP" dialog.
|
| 452 |
|
|
In the figure above the resulting IP block is named "neorv32_top_axi4lite_v1_0".
|
| 453 |
|
|
*(Note: Use Syntheiss option "global" when generating the block design to maintain the internal TWI tri-state drivers.)*
|
| 454 |
|
|
|
| 455 |
|
|
The setup uses an AXI interconnect to attach two block RAMs to the processor. Since the processor in this example is configured *without* IMEM and DMEM,
|
| 456 |
|
|
the attached block RAMs are used for storing instructions and data: the first RAM is used as instruction memory
|
| 457 |
|
|
and is mapped to address `0x00000000 - 0x00003fff` (16kB), the second RAM is used as data memory and is mapped to address `0x80000000 - 0x80001fff` (8kB).
|
| 458 |
|
|
|
| 459 |
|
|
|
| 460 |
|
|
|
| 461 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
## Getting Started
|
| 462 |
|
|
|
| 463 |
|
|
This overview is just a short excerpt from the *Let's Get It Started* section of the NEORV32 documentary:
|
| 464 |
|
|
|
| 465 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf)
|
| 466 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 467 |
|
|
|
| 468 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
### 1. Get the Toolchain
|
| 469 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 470 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
At first you need a **RISC-V GCC toolchain**. You can either [download the sources](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain)
|
| 471 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
and build the toolchain by yourself, or you can download a prebuilt one and install it.
|
| 472 |
|
|
|
| 473 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
To build the toolchain by yourself, follow the official [build instructions](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain).
|
| 474 |
14 |
zero_gravi |
Make sure to use the `ilp32` or `ilp32e` ABI.
|
| 475 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 476 |
15 |
zero_gravi |
**Alternatively**, you can download a prebuilt toolchain. I have uploaded the toolchains I am using to GitHub. These toolchains
|
| 477 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
were compiled on a 64-bit x86 Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (Ubuntu on Windows, actually). Download the toolchain of choice:
|
| 478 |
46 |
zero_gravi |
[:octocat: github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt)
|
| 479 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 480 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
You can also use the toolchains provided by [SiFive](https://github.com/sifive/freedom-tools/releases). These are 64-bit toolchains that can also emit 32-bit
|
| 481 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
RISC-V code. They were compiled for more sophisticated machines (`rv32imac`) so make sure the according NEORV32 hardware extensions are enabled.
|
| 482 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 483 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
:warning: Keep in mind that – for instance – a `rv32imc` toolchain only provides library code compiled with compressed and
|
| 484 |
|
|
`mul`/`div` instructions! Hence, this code cannot be executed (without emulation) on an architecture without these extensions!
|
| 485 |
|
|
|
| 486 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
To check everything works fine, make sure `GNU Make` and a native `GCC` compiler are installed.
|
| 487 |
|
|
Test the installation of the RISC-V toolchain by navigating to an [example program project](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example) like
|
| 488 |
|
|
`sw/example/blink_led` and running:
|
| 489 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 490 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make check
|
| 491 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 492 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 493 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
### 2. Download the NEORV32 Project
|
| 494 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 495 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
Get the sources of the NEORV32 Processor project. The simplest way is using `git clone` (suggested for easy project updates via `git pull`):
|
| 496 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 497 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
$ git clone https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32.git
|
| 498 |
|
|
|
| 499 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
Alternatively, you can either download a specific [release](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases) or get the most recent version
|
| 500 |
|
|
of this project as [`*.zip` file](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/archive/master.zip).
|
| 501 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 502 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 503 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
### 3. Create a new FPGA Project
|
| 504 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 505 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
Create a new project with your FPGA design tool of choice. Add all the `*.vhd` files from the [`rtl/core`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl)
|
| 506 |
|
|
folder to this project. Make sure to add these files to a **new design library** called `neorv32`.
|
| 507 |
|
|
|
| 508 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
You can either instantiate the [processor's top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) or one of its
|
| 509 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
[wrappers](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates) in your own project. If you just want to try thing out,
|
| 510 |
|
|
you can use the simple [**test setup** (`rtl/top_templates/neorv32_test_setup.vhd`)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates/neorv32_test_setup.vhd) as top entity.
|
| 511 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 512 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 513 |
|
|
|
| 514 |
|
|
|
| 515 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
This test setup instantiates the processor and implements most of the peripherals and some ISA extensions. Only the UART0 communications lines, clock, reset and some
|
| 516 |
|
|
GPIO output signals are propagated as actual top entity interface signals. Basically, it is a FPGA version of a "hello world" example:
|
| 517 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 518 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
```vhdl
|
| 519 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
entity neorv32_test_setup is
|
| 520 |
|
|
port (
|
| 521 |
|
|
-- Global control --
|
| 522 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
clk_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global clock, rising edge
|
| 523 |
|
|
rstn_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global reset, low-active, async
|
| 524 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
-- GPIO --
|
| 525 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
gpio_o : out std_ulogic_vector(7 downto 0); -- parallel output
|
| 526 |
|
|
-- UART0 --
|
| 527 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
uart0_txd_o : out std_ulogic; -- UART0 send data
|
| 528 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
uart0_rxd_i : in std_ulogic := '0' -- UART0 receive data
|
| 529 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
);
|
| 530 |
|
|
end neorv32_test_setup;
|
| 531 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
```
|
| 532 |
|
|
|
| 533 |
|
|
|
| 534 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
### 4. Compile an Example Program
|
| 535 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 536 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
The NEORV32 project includes several [example program project](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example) from
|
| 537 |
|
|
which you can start your own application. There are example programs to check out the processor's peripheral like I2C or the true-random number generator.
|
| 538 |
|
|
And yes, there is also a port of [Conway's Game of Life](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/game_of_life) available! :wink:
|
| 539 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 540 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
Simply compile one of these projects using
|
| 541 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 542 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make clean_all exe
|
| 543 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 544 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
This will create a NEORV32 *executable* `neorv32_exe.bin` in the same folder, which you can upload via the bootloader.
|
| 545 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 546 |
|
|
|
| 547 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
### 5. Upload the Executable via the Bootloader
|
| 548 |
34 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 549 |
50 |
zero_gravi |
Connect your FPGA board via UART to your computer and open the according port to interface with the fancy NEORV32 bootloader. The bootloader
|
| 550 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
uses the following default UART configuration:
|
| 551 |
|
|
|
| 552 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
* 19200 Baud
|
| 553 |
|
|
* 8 data bits
|
| 554 |
|
|
* 1 stop bit
|
| 555 |
|
|
* No parity bits
|
| 556 |
|
|
* No transmission / flow control protocol (raw bytes only)
|
| 557 |
|
|
* Newline on `\r\n` (carriage return & newline) - also for sent data
|
| 558 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 559 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
Use the bootloader console to upload the `neorv32_exe.bin` executable gerated during application compiling and *run* your application.
|
| 560 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 561 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
```
|
| 562 |
43 |
zero_gravi |
<< NEORV32 Bootloader >>
|
| 563 |
|
|
|
| 564 |
|
|
BLDV: Nov 7 2020
|
| 565 |
|
|
HWV: 0x01040606
|
| 566 |
|
|
CLK: 0x0134FD90 Hz
|
| 567 |
|
|
USER: 0x0001CE40
|
| 568 |
|
|
MISA: 0x42801104
|
| 569 |
|
|
PROC: 0x03FF0035
|
| 570 |
|
|
IMEM: 0x00010000 bytes @ 0x00000000
|
| 571 |
|
|
DMEM: 0x00010000 bytes @ 0x80000000
|
| 572 |
|
|
|
| 573 |
|
|
Autoboot in 8s. Press key to abort.
|
| 574 |
|
|
Aborted.
|
| 575 |
|
|
|
| 576 |
|
|
Available CMDs:
|
| 577 |
|
|
h: Help
|
| 578 |
|
|
r: Restart
|
| 579 |
|
|
u: Upload
|
| 580 |
|
|
s: Store to flash
|
| 581 |
|
|
l: Load from flash
|
| 582 |
|
|
e: Execute
|
| 583 |
|
|
CMD:> u
|
| 584 |
|
|
Awaiting neorv32_exe.bin... OK
|
| 585 |
|
|
CMD:> e
|
| 586 |
|
|
Booting...
|
| 587 |
|
|
|
| 588 |
|
|
Blinking LED demo program
|
| 589 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
```
|
| 590 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 591 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
Going further: Take a look at the _Let's Get It Started!_ chapter of the [:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
| 592 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 593 |
|
|
|
| 594 |
|
|
|
| 595 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
## Contribute/Feedback/Questions
|
| 596 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 597 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
I'm always thankful for help! So if you have any questions, bug reports, ideas or if you want to give any kind of feedback, feel free
|
| 598 |
|
|
to [open a new issue](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/issues), start a new [discussion on GitHub](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/discussions)
|
| 599 |
|
|
or directly [drop me a line](mailto:stnolting@gmail.com).
|
| 600 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 601 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
Here is a simple guide line if you'd like to contribute to this repository:
|
| 602 |
22 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 603 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
0. :star: this repository :wink:
|
| 604 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
1. Check out the project's [code of conduct](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md)
|
| 605 |
|
|
2. [Fork](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/fork) this repository and clone the fork
|
| 606 |
|
|
3. Create a feature branch in your fork: `git checkout -b awesome_new_feature_branch`
|
| 607 |
|
|
4. Create a new remote for the upstream repo: `git remote add upstream https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32`
|
| 608 |
|
|
5. Commit your modifications: `git commit -m "Awesome new feature!"`
|
| 609 |
|
|
6. Push to the branch: `git push origin awesome_new_feature_branch`
|
| 610 |
|
|
7. Create a new [pull request](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/pulls)
|
| 611 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 612 |
40 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 613 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
## Legal
|
| 614 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 615 |
12 |
zero_gravi |
This project is released under the BSD 3-Clause license. No copyright infringement intended.
|
| 616 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
Other implied or used projects might have different licensing - see their documentation to get more information.
|
| 617 |
|
|
|
| 618 |
37 |
zero_gravi |
#### Citing
|
| 619 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 620 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
If you are using the NEORV32 or parts of the project in some kind of publication, please cite it as follows:
|
| 621 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 622 |
51 |
zero_gravi |
> S. Nolting, "The NEORV32 RISC-V Processor", github.com/stnolting/neorv32
|
| 623 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 624 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
#### BSD 3-Clause License
|
| 625 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 626 |
42 |
zero_gravi |
Copyright (c) 2021, Stephan Nolting. All rights reserved.
|
| 627 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 628 |
|
|
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are
|
| 629 |
|
|
permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
|
| 630 |
|
|
|
| 631 |
|
|
1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of
|
| 632 |
|
|
conditions and the following disclaimer.
|
| 633 |
|
|
2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of
|
| 634 |
|
|
conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials
|
| 635 |
|
|
provided with the distribution.
|
| 636 |
|
|
3. Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its contributors may be used to
|
| 637 |
|
|
endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written
|
| 638 |
|
|
permission.
|
| 639 |
|
|
|
| 640 |
|
|
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS
|
| 641 |
|
|
OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
|
| 642 |
|
|
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
|
| 643 |
|
|
COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL,
|
| 644 |
|
|
EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE
|
| 645 |
|
|
GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED
|
| 646 |
|
|
AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING
|
| 647 |
|
|
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED
|
| 648 |
|
|
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
|
| 649 |
|
|
|
| 650 |
|
|
|
| 651 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
#### Limitation of Liability for External Links
|
| 652 |
|
|
|
| 653 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
Our website contains links to the websites of third parties ("external links"). As the
|
| 654 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
content of these websites is not under our control, we cannot assume any liability for
|
| 655 |
|
|
such external content. In all cases, the provider of information of the linked websites
|
| 656 |
|
|
is liable for the content and accuracy of the information provided. At the point in time
|
| 657 |
|
|
when the links were placed, no infringements of the law were recognisable to us. As soon
|
| 658 |
|
|
as an infringement of the law becomes known to us, we will immediately remove the
|
| 659 |
|
|
link in question.
|
| 660 |
|
|
|
| 661 |
|
|
|
| 662 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
#### Proprietary Notice
|
| 663 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 664 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
"Artix" and "Vivado" are trademarks of Xilinx Inc.
|
| 665 |
|
|
|
| 666 |
45 |
zero_gravi |
"Cyclone" and "Quartus Prime Lite" are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
|
| 667 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 668 |
35 |
zero_gravi |
"iCE40", "UltraPlus" and "Radiant" are trademarks of Lattice Semiconductor Corporation.
|
| 669 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 670 |
35 |
zero_gravi |
"AXI", "AXI4" and "AXI4-Lite" are trademarks of Arm Holdings plc.
|
| 671 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 672 |
|
|
|
| 673 |
|
|
|
| 674 |
18 |
zero_gravi |
## Acknowledgements
|
| 675 |
9 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 676 |
18 |
zero_gravi |
[](https://riscv.org/)
|
| 677 |
|
|
|
| 678 |
23 |
zero_gravi |
[RISC-V](https://riscv.org/) - Instruction Sets Want To Be Free!
|
| 679 |
11 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 680 |
43 |
zero_gravi |
Continous integration provided by [:octocat: GitHub Actions](https://github.com/features/actions) and powered by [GHDL](https://github.com/ghdl/ghdl).
|
| 681 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 682 |
|
|

|
| 683 |
|
|
|
| 684 |
|
|
This project is not affiliated with or endorsed by the Open Source Initiative (https://www.oshwa.org / https://opensource.org).
|
| 685 |
|
|
|
| 686 |
32 |
zero_gravi |
--------
|
| 687 |
2 |
zero_gravi |
|
| 688 |
36 |
zero_gravi |
Made with :coffee: in Hannover, Germany :eu:
|
