| Line 25... |
Line 25... |
on the RISC-V-compliant NEORV32 CPU. The project consists of two main parts:
|
on the RISC-V-compliant NEORV32 CPU. The project consists of two main parts:
|
|
|
|
|
### [NEORV32 CPU](#CPU-Features)
|
### [NEORV32 CPU](#CPU-Features)
|
|
|
The CPU implements an `rv32i RISC-V` core with optional `C`, `E`, `M`, `U`, `Zicsr`, `Zifencei` and
|
The CPU implements a `rv32i RISC-V` core with optional `C`, `E`, `M`, `U`, `Zicsr`, `Zifencei` and
|
`PMP` (physical memory protection) extensions. It passes the official [RISC-V compliance tests](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance)
|
`PMP` (physical memory protection) extensions. It passes the official [RISC-V compliance tests](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance)
|
and is compliant to the *Unprivileged ISA Specification [Version 2.2](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-privileged.pdf)*
|
and is compliant to the *Unprivileged ISA Specification [Version 2.2](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-privileged.pdf)*
|
and a subset of the *Privileged Architecture Specification [Version 1.12-draft](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)*.
|
and a subset of the *Privileged Architecture Specification [Version 1.12-draft](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)*.
|
|
|
If you do not want to use the NEORV32 Processor setup, you can also use the CPU in
|
If you do not want to use the NEORV32 Processor setup, you can also use the CPU in
|
| Line 50... |
Line 50... |
|
|
This project comes with a complete software ecosystem that features core
|
This project comes with a complete software ecosystem that features core
|
libraries for high-level usage of the provided functions and peripherals,
|
libraries for high-level usage of the provided functions and peripherals,
|
makefiles, a runtime environment, several example programs to start with - including a free RTOS demo - and
|
makefiles, a runtime environment, several example programs to start with - including a free RTOS demo - and
|
even a builtin bootloader for easy program upload via UART.
|
even a builtin bootloader for easy program upload via UART.
|
All software source files provide a doxygen-based documentary (available on [GitHub pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html)).
|
|
|
|
|
|
### [How to get started?](#Getting-Started)
|
### [How to get started?](#Getting-Started)
|
|
|
The processor is intended to work "out of the box". Just synthesize the
|
The processor is intended to work "out of the box". Just synthesize the
|
[test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project), upload it to your FPGA board of choice and start playing
|
[test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project), upload it to your FPGA board of choice and start playing
|
with the NEORV32. If you do not want to [compile the GCC toolchains](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain) by yourself, you can also
|
with the NEORV32. For more information take a look at the [NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf).
|
download [pre-compiled toolchains](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt) for Linux.
|
|
|
|
For more information take a look at the [ NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
The project’s change log is available in the [CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) file in the root directory of this repository.
|
|
To see the changes between releases visit the project's [release page](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases).
|
|
|
|
|
### Key Features
|
### Key Features
|
|
|
* RISC-V-compliant `rv32i` CPU with optional `C`, `E`, `M`, `U`, `Zicsr`, `Zifencei` and `PMP` (physical memory protection) extensions
|
* RISC-V-compliant `rv32i` CPU with optional `C`, `E`, `M`, `U`, `Zicsr`, `Zifencei` and `PMP` (physical memory protection) extensions
|
* GCC-based toolchain ([pre-compiled rv32i and rv32e toolchains available](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt))
|
* GCC-based toolchain ([pre-compiled rv32i and rv32e toolchains available](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt))
|
* Application compilation based on [GNU makefiles](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/blink_led/makefile)
|
* Application compilation based on [GNU makefiles](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/blink_led/makefile)
|
* [Doxygen-based](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/doxygen_makefile_sw) documentation of the software framework: available on [GitHub pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html)
|
* [Doxygen-based](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/doxygen_makefile_sw) documentation of the software framework: available on [GitHub pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html)
|
* [**Detailed data sheet**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf)
|
* [**Full-blown data sheet**](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf)
|
* Completely described in behavioral, platform-independent VHDL - no primitives, macros, etc.
|
* Completely described in behavioral, platform-independent VHDL - no primitives, macros, etc.
|
* Fully synchronous design, no latches, no gated clocks
|
* Fully synchronous design, no latches, no gated clocks
|
* Small hardware footprint and high operating frequency
|
* Small hardware footprint and high operating frequency
|
* Highly configurable CPU and processor setup
|
* Highly configurable CPU and processor setup
|
* [FreeRTOS port](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/demo_freeRTOS) available
|
* [FreeRTOS port](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/demo_freeRTOS) available
|
| Line 94... |
Line 93... |
The processor is [synthesizable](#FPGA-Implementation-Results) (tested on *real hardware* using Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx Vivado and Lattice Radiant/Synplify Pro) and can successfully execute
|
The processor is [synthesizable](#FPGA-Implementation-Results) (tested on *real hardware* using Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx Vivado and Lattice Radiant/Synplify Pro) and can successfully execute
|
all the [provided example programs](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example) including the [CoreMark benchmark](#CoreMark-Benchmark).
|
all the [provided example programs](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example) including the [CoreMark benchmark](#CoreMark-Benchmark).
|
|
|
The processor passes the official `rv32i`, `rv32im`, `rv32imc`, `rv32Zicsr` and `rv32Zifencei` [RISC-V compliance tests](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-compliance).
|
The processor passes the official `rv32i`, `rv32im`, `rv32imc`, `rv32Zicsr` and `rv32Zifencei` [RISC-V compliance tests](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-compliance).
|
|
|
The project’s change log is available in the [CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) file in the root directory of this repository.
|
|
|
|
| Project component | CI status | Note |
|
| Project component | CI status | Note |
|
|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------|:---------|
|
|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------|:---------|
|
| [NEORV32 processor](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/neorv32) | [](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) |
|
| [NEORV32 processor](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/neorv32) | [](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) |
|
| [Pre-built toolchain](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt) | |
|
| [Pre-built toolchain](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/riscv_gcc_prebuilt) | |
|
| [RISC-V compliance test](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance) | |
|
| [RISC-V compliance test](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance) | [](https://travis-ci.com/stnolting/neorv32_riscv_compliance) | |
|
|
|
|
|
### To-Do / Wish List
|
### To-Do / Wish List
|
|
|
|
* Further size and performance optimization
|
* Add AXI(-Lite) bridges
|
* Add AXI(-Lite) bridges
|
* Synthesis results (+ wrappers?) for more platforms
|
* Synthesis results (+ wrappers?) for more platforms
|
* Maybe port additional RTOSs (like [Zephyr](https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr) or [RIOT](https://www.riot-os.org))
|
* Maybe port additional RTOSs (like [Zephyr](https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr) or [RIOT](https://www.riot-os.org))
|
|
* Use LaTeX for data sheet
|
* Implement further CPU extensions:
|
* Implement further CPU extensions:
|
* Atomic operations (`A`)
|
* Atomic operations (`A`)
|
* Bitmanipulation operations (`B`), when they are "official"
|
* Bitmanipulation operations (`B`), when they are "official"
|
* Floating-point instructions (`F`)
|
* Floating-point instructions (`F`)
|
* ...
|
* ...
|
|
|
|
|
## Features
|
## Features
|
|
|
The full-blown data sheet of the NEORV32 Processor/CPU is available as pdf file:
|
The full-blown data sheet of the NEORV32 Processor and CPU is available as pdf file:
|
[ NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
[ NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
|
|
### Processor Features
|
### Processor Features
|
|
|
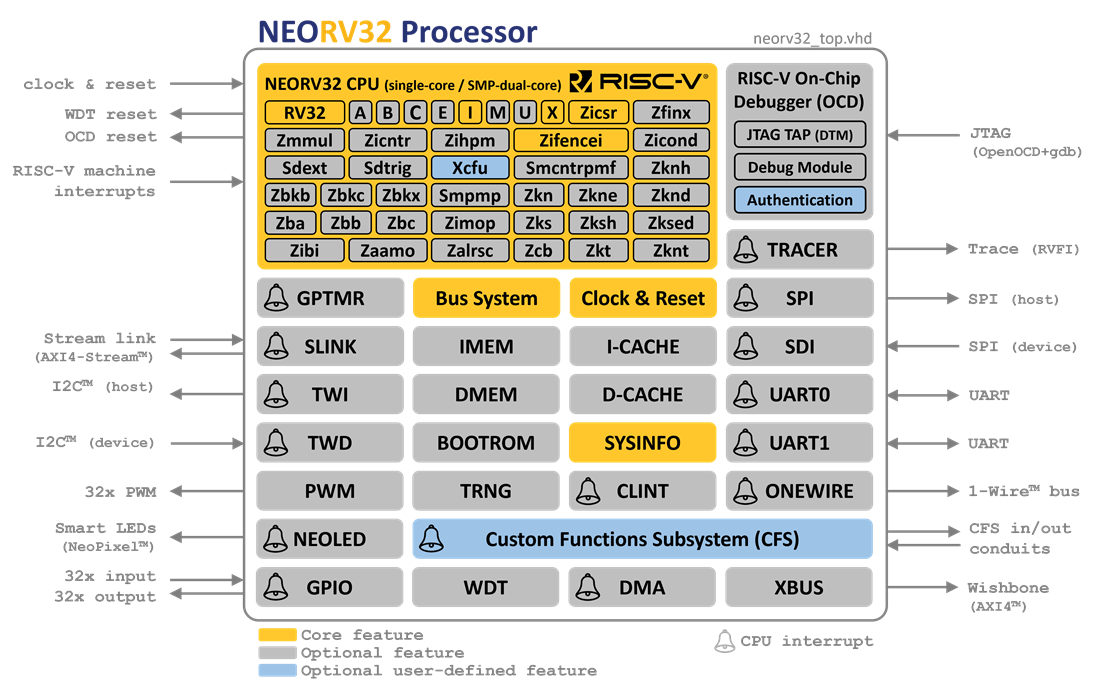
|

|
| Line 138... |
Line 137... |
* Optional general purpose parallel IO port (**GPIO**), 32xOut & 32xIn, with pin-change interrupt
|
* Optional general purpose parallel IO port (**GPIO**), 32xOut & 32xIn, with pin-change interrupt
|
* Optional 32-bit external bus interface, Wishbone b4 compliant (**WISHBONE**), *standard* or *pipelined* handshake/transactions mode
|
* Optional 32-bit external bus interface, Wishbone b4 compliant (**WISHBONE**), *standard* or *pipelined* handshake/transactions mode
|
* Optional watchdog timer (**WDT**)
|
* Optional watchdog timer (**WDT**)
|
* Optional PWM controller with 4 channels and 8-bit duty cycle resolution (**PWM**)
|
* Optional PWM controller with 4 channels and 8-bit duty cycle resolution (**PWM**)
|
* Optional GARO-based true random number generator (**TRNG**)
|
* Optional GARO-based true random number generator (**TRNG**)
|
* Optional custom functions unit (**CFU**) for tightly-coupled custom co-processors
|
* Optional custom functions units (**CFU0** and **CFU1**) for tightly-coupled custom co-processors
|
* System configuration information memory to check hardware configuration by software (**SYSINFO**)
|
* System configuration information memory to check hardware configuration by software (**SYSINFO**)
|
|
|
### CPU Features
|
### CPU Features
|
|
|
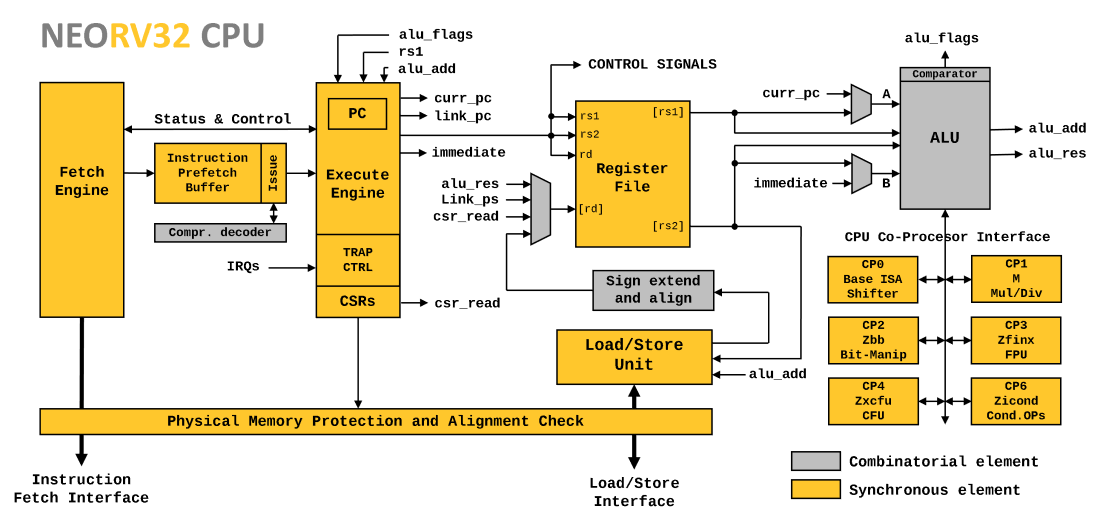
|

|
| Line 239... |
Line 238... |
This chapter shows exemplary implementation results of the NEORV32 CPU for an **Intel Cyclone IV EP4CE22F17C6N FPGA** on
|
This chapter shows exemplary implementation results of the NEORV32 CPU for an **Intel Cyclone IV EP4CE22F17C6N FPGA** on
|
a DE0-nano board. The design was synthesized using **Intel Quartus Prime Lite 19.1** ("balanced implementation"). The timing
|
a DE0-nano board. The design was synthesized using **Intel Quartus Prime Lite 19.1** ("balanced implementation"). The timing
|
information is derived from the Timing Analyzer / Slow 1200mV 0C Model. If not otherwise specified, the default configuration
|
information is derived from the Timing Analyzer / Slow 1200mV 0C Model. If not otherwise specified, the default configuration
|
of the CPU's generics is assumed (for example no PMP). No constraints were used at all.
|
of the CPU's generics is assumed (for example no PMP). No constraints were used at all.
|
|
|
Results generated for hardware version: `1.4.4.8`
|
Results generated for hardware version `1.4.4.8`.
|
|
|
| CPU Configuration | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs | f_max |
|
| CPU Configuration | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs | f_max |
|
|:---------------------------------------|:----------:|:--------:|:-----------:|:----:|:--------:|
|
|:---------------------------------------|:----------:|:--------:|:-----------:|:----:|:--------:|
|
| `rv32i` | 983 | 438 | 2048 | 0 | ~120 MHz |
|
| `rv32i` | 983 | 438 | 2048 | 0 | ~120 MHz |
|
| `rv32i` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 1877 | 802 | 2048 | 0 | ~112 MHz |
|
| `rv32i` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 1877 | 802 | 2048 | 0 | ~112 MHz |
|
| Line 252... |
Line 251... |
| `rv32emc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 2680 | 1061 | 1024 | 0 | ~110 MHz |
|
| `rv32emc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 2680 | 1061 | 1024 | 0 | ~110 MHz |
|
|
|
|
|
### NEORV32 Processor-Internal Peripherals and Memories
|
### NEORV32 Processor-Internal Peripherals and Memories
|
|
|
Results generated for hardware version: `1.4.4.8`
|
Results generated for hardware version `1.4.4.8`.
|
|
|
| Module | Description | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs |
|
| Module | Description | LEs | FFs | Memory bits | DSPs |
|
|:----------|:-----------------------------------------------------|----:|----:|------------:|-----:|
|
|:----------|:-----------------------------------------------------|----:|----:|------------:|-----:|
|
| BOOT ROM | Bootloader ROM (default 4kB) | 4 | 1 | 32 768 | 0 |
|
| BOOT ROM | Bootloader ROM (default 4kB) | 4 | 1 | 32 768 | 0 |
|
| BUSSWITCH | Mux for CPU I & D interfaces | 62 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
|
| BUSSWITCH | Mux for CPU I & D interfaces | 62 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
|
| CFU | Custom functions unit | - | - | - | - |
|
| CFU0 | Custom functions unit 0 | - | - | - | - |
|
|
| CFU1 | Custom functions unit 1 | - | - | - | - |
|
| DMEM | Processor-internal data memory (default 8kB) | 13 | 2 | 65 536 | 0 |
|
| DMEM | Processor-internal data memory (default 8kB) | 13 | 2 | 65 536 | 0 |
|
| GPIO | General purpose input/output ports | 66 | 65 | 0 | 0 |
|
| GPIO | General purpose input/output ports | 66 | 65 | 0 | 0 |
|
| IMEM | Processor-internal instruction memory (default 16kb) | 7 | 2 | 131 072 | 0 |
|
| IMEM | Processor-internal instruction memory (default 16kb) | 7 | 2 | 131 072 | 0 |
|
| MTIME | Machine system timer | 268 | 166 | 0 | 0 |
|
| MTIME | Machine system timer | 268 | 166 | 0 | 0 |
|
| PWM | Pulse-width modulation controller | 72 | 69 | 0 | 0 |
|
| PWM | Pulse-width modulation controller | 72 | 69 | 0 | 0 |
|
| Line 275... |
Line 275... |
| WISHBONE | External memory interface (`MEM_EXT_REG_STAGES` = 2) | 106 | 104 | 0 | 0 |
|
| WISHBONE | External memory interface (`MEM_EXT_REG_STAGES` = 2) | 106 | 104 | 0 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
### NEORV32 Processor - Exemplary FPGA Setups
|
### NEORV32 Processor - Exemplary FPGA Setups
|
|
|
Exemplary processor implementation results for different FPGA platforms. The processor setup uses *the default peripheral configuration* (like no _CFU_ and no _TRNG_),
|
Exemplary processor implementation results for different FPGA platforms. The processor setup uses *the default peripheral configuration* (like no _CFUs_ and no _TRNG_),
|
no external memory interface and only internal instruction and data memories. IMEM uses 16kB and DMEM uses 8kB memory space. The setup's top entity connects most of the
|
no external memory interface and only internal instruction and data memories. IMEM uses 16kB and DMEM uses 8kB memory space. The setup's top entity connects most of the
|
processor's [top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) signals
|
processor's [top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) signals
|
to FPGA pins - except for the Wishbone bus and the interrupt signals.
|
to FPGA pins - except for the Wishbone bus and the interrupt signals.
|
|
|
Results generated for hardware version: `1.4.4.8`
|
Results generated for hardware version `1.4.4.8`.
|
|
|
| Vendor | FPGA | Board | Toolchain | Strategy | CPU Configuration | LUT / LE | FF / REG | DSP | Memory Bits | BRAM / EBR | SPRAM | Frequency |
|
| Vendor | FPGA | Board | Toolchain | Strategy | CPU Configuration | LUT / LE | FF / REG | DSP | Memory Bits | BRAM / EBR | SPRAM | Frequency |
|
|:--------|:----------------------------------|:-----------------|:---------------------------|:-------- |:-----------------------------------------------|:-----------|:-----------|:-------|:-------------|:-----------|:---------|--------------:|
|
|:--------|:----------------------------------|:-----------------|:---------------------------|:-------- |:-----------------------------------------------|:-----------|:-----------|:-------|:-------------|:-----------|:---------|--------------:|
|
| Intel | Cyclone IV `EP4CE22F17C6N` | Terasic DE0-Nano | Quartus Prime Lite 19.1 | balanced | `rv32imc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` + `PMP` | 4008 (18%) | 1849 (9%) | 0 (0%) | 231424 (38%) | - | - | 105 MHz |
|
| Intel | Cyclone IV `EP4CE22F17C6N` | Terasic DE0-Nano | Quartus Prime Lite 19.1 | balanced | `rv32imc` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` + `PMP` | 4008 (18%) | 1849 (9%) | 0 (0%) | 231424 (38%) | - | - | 105 MHz |
|
| Lattice | iCE40 UltraPlus `iCE40UP5K-SG48I` | Upduino v2.0 | Radiant 2.1 (Synplify Pro) | default | `rv32ic` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 4296 (81%) | 1611 (30%) | 0 (0%) | - | 12 (40%) | 4 (100%) | *c* 22.5 MHz |
|
| Lattice | iCE40 UltraPlus `iCE40UP5K-SG48I` | Upduino v2.0 | Radiant 2.1 (Synplify Pro) | default | `rv32ic` + `u` + `Zicsr` + `Zifencei` | 4296 (81%) | 1611 (30%) | 0 (0%) | - | 12 (40%) | 4 (100%) | *c* 22.5 MHz |
|
| Line 306... |
Line 306... |
|
|
The [CoreMark CPU benchmark](https://www.eembc.org/coremark) was executed on the NEORV32 and is available in the
|
The [CoreMark CPU benchmark](https://www.eembc.org/coremark) was executed on the NEORV32 and is available in the
|
[sw/example/coremark](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/coremark) project folder. This benchmark
|
[sw/example/coremark](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/sw/example/coremark) project folder. This benchmark
|
tests the capabilities of a CPU itself rather than the functions provided by the whole system / SoC.
|
tests the capabilities of a CPU itself rather than the functions provided by the whole system / SoC.
|
|
|
Results generated for hardware version: `1.4.4.8`
|
Results generated for hardware version `1.4.5.4`.
|
|
|
~~~
|
~~~
|
**Configuration**
|
**Configuration**
|
Hardware: 32kB IMEM, 16kB DMEM, 100MHz clock
|
Hardware: 32kB IMEM, 16kB DMEM, 100MHz clock
|
CoreMark: 2000 iterations, MEM_METHOD is MEM_STACK
|
CoreMark: 2000 iterations, MEM_METHOD is MEM_STACK
|
| Line 318... |
Line 318... |
Flags: default, see makefile
|
Flags: default, see makefile
|
Peripherals: UART for printing the results
|
Peripherals: UART for printing the results
|
~~~
|
~~~
|
|
|
| CPU | Executable Size | Optimization | CoreMark Score | CoreMarks/MHz |
|
| CPU | Executable Size | Optimization | CoreMark Score | CoreMarks/MHz |
|
|:--------------------------|:---------------:|:------------:|:--------------:|:-------------:|
|
|:--------------------------------------------|:---------------:|:------------:|:--------------:|:-------------:|
|
| `rv32i` | 26 940 bytes | `-O3` | 33.89 | **0.3389** |
|
| `rv32i` | 26 940 bytes | `-O3` | 33.89 | **0.3389** |
|
| `rv32im` | 25 772 bytes | `-O3` | 64.51 | **0.6451** |
|
| `rv32im` | 25 772 bytes | `-O3` | 64.51 | **0.6451** |
|
| `rv32imc` | 20 524 bytes | `-O3` | 64.51 | **0.6451** |
|
| `rv32imc` | 20 524 bytes | `-O3` | 64.51 | **0.6451** |
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 20 524 bytes | `-O3` | 80.00 | **0.8000** |
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 20 524 bytes | `-O3` | 80.00 | **0.8000** |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` + `FAST_SHIFT_EN` | 20 524 bytes | `-O3` | 83.33 | **0.8333** |
|
|
|
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic).
|
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic). The `FAST_SHIFT_EN` configuration
|
|
uses a barrel shifter for CPU shift operations (enabled via the `FAST_SHIFT_EN` generic).
|
|
|
When the `C` extension is enabled, branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
When the `C` extension is enabled, branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
|
|
|
|
### Instruction Cycles
|
### Instruction Cycles
|
|
|
The NEORV32 CPU is based on a two-stages pipelined architecutre. Each stage uses a multi-cycle processing scheme. Hence,
|
The NEORV32 CPU is based on a two-stages pipelined architecutre. Each stage uses a multi-cycle processing scheme. Hence,
|
each instruction requires several clock cycles to execute (2 cycles for ALU operations, ..., 40 cycles for divisions).
|
each instruction requires several clock cycles to execute (2 cycles for ALU operations, ..., 40 cycles for divisions).
|
The average CPI (cycles per instruction) depends on the instruction mix of a specific applications and also on the available
|
The average CPI (cycles per instruction) depends on the instruction mix of a specific applications and also on the available
|
CPU extensions.
|
CPU extensions.
|
|
|
Please note that the CPU-internal shifter (e.g. for the `SLL` instruction) as well as the multiplier and divider of the
|
Please note that by default the CPU-internal shifter (e.g. for the `SLL` instruction) as well as the multiplier and divider of the
|
`M` extension use a bit-serial approach and require several cycles for completion.
|
`M` extension use a bit-serial approach and require several cycles for completion.
|
|
|
The following table shows the performance results for successfully running 2000 CoreMark
|
The following table shows the performance results for successfully running 2000 CoreMark
|
iterations, which reflects a pretty good "real-life" work load. The average CPI is computed by
|
iterations, which reflects a pretty good "real-life" work load. The average CPI is computed by
|
dividing the total number of required clock cycles (only the timed core to avoid distortion due to IO wait cycles; sampled via the `cycle[h]` CSRs)
|
dividing the total number of required clock cycles (only the timed core to avoid distortion due to IO wait cycles; sampled via the `cycle[h]` CSRs)
|
by the number of executed instructions (`instret[h]` CSRs). The executables were generated using optimization `-O3`.
|
by the number of executed instructions (`instret[h]` CSRs). The executables were generated using optimization `-O3`.
|
|
|
Results generated for hardware version: `1.4.4.8`
|
Results generated for hardware version `1.4.5.4`.
|
|
|
| CPU | Required Clock Cycles | Executed Instructions | Average CPI |
|
| CPU | Required Clock Cycles | Executed Instructions | Average CPI |
|
|:--------------------------|----------------------:|----------------------:|:-----------:|
|
|:--------------------------------------------|----------------------:|----------------------:|:-----------:|
|
| `rv32i` | 5 945 938 586 | 1 469 587 406 | **4.05** |
|
| `rv32i` | 5 945 938 586 | 1 469 587 406 | **4.05** |
|
| `rv32im` | 3 110 282 586 | 602 225 760 | **5.16** |
|
| `rv32im` | 3 110 282 586 | 602 225 760 | **5.16** |
|
| `rv32imc` | 3 172 969 968 | 615 388 924 | **5.16** |
|
| `rv32imc` | 3 172 969 968 | 615 388 890 | **5.16** |
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 2 590 417 968 | 615 388 890 | **4.21** |
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` | 2 590 417 968 | 615 388 890 | **4.21** |
|
|
| `rv32imc` + `FAST_MUL_EN` + `FAST_SHIFT_EN` | 2 456 318 408 | 615 388 890 | **3.99** |
|
|
|
|
|
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic).
|
The `FAST_MUL_EN` configuration uses DSPs for the multiplier of the `M` extension (enabled via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic). The `FAST_SHIFT_EN` configuration
|
|
uses a barrel shifter for CPU shift operations (enabled via the `FAST_SHIFT_EN` generic).
|
|
|
When the `C` extension is enabled, branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
When the `C` extension is enabled, branches to an unaligned uncompressed instruction require additional instruction fetch cycles.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Top Entities
|
## Top Entities
|
|
|
The top entity of the **NEORV32 Processor** is [**neorv32_top.vhd**](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) (from `rtl/core`).
|
The top entity of the **NEORV32 Processor** (SoC) is [**neorv32_top.vhd**](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd)
|
Just instantiate this file in your project and you are ready to go! All signals of this top entity are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively
|
and the top entity of the **NEORV32 CPU** is [**neorv32_cpu.vhd**](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_cpu.vhd). Both
|
(except for the TWI signals, which are of type *std_logic*).
|
top entities are located in `rtl/core`.
|
|
|
The top entity of the **NEORV32 CPU** is [**neorv32_cpu.vhd**](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_cpu.vhd) (from `rtl/core`).
|
All signals of the top entities are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively
|
All signals of this top entity are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively.
|
(except for the processor's TWI signals, which are of type *std_logic*). Leave all unused output ports unconnected (`open`) and tie all unused
|
|
input ports to zero (`'0'` or `(others => '0')`, respectively).
|
Use the generics to configure the processor/CPU according to your needs. Each generic is initilized with the default configuration.
|
|
Detailed information regarding the signals and configuration generics can be found in
|
|
the [NEORV32 documentary](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
|
|
|
Alternative top entities, like the simplified ["hello world" test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project) or CPU/Processor
|
Alternative top entities, like the simplified ["hello world" test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project) or CPU/Processor
|
wrappers with resolved port signal types (i.e. *std_logic*), can be found in [`rtl/top_templates`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates).
|
wrappers with resolved port signal types (i.e. *std_logic*), can be found in [`rtl/top_templates`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates).
|
|
|
|
Use the top's generics to configure the processor/CPU according to your needs. Each generic is initilized with the default configuration.
|
|
Detailed information regarding the interface signals and configuration generics can be found in
|
|
the [NEORV32 documentary](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
|
|
### NEORV32 CPU
|
### NEORV32 CPU
|
|
|
```vhdl
|
```vhdl
|
entity neorv32_cpu is
|
entity neorv32_cpu is
|
| Line 392... |
Line 398... |
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_U : boolean := false; -- implement user mode extension?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_U : boolean := false; -- implement user mode extension?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zicsr : boolean := true; -- implement CSR system?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zicsr : boolean := true; -- implement CSR system?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zifencei : boolean := true; -- implement instruction stream sync.?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zifencei : boolean := true; -- implement instruction stream sync.?
|
-- Extension Options --
|
-- Extension Options --
|
FAST_MUL_EN : boolean := false; -- use DSPs for M extension's multiplier
|
FAST_MUL_EN : boolean := false; -- use DSPs for M extension's multiplier
|
|
FAST_SHIFT_EN : boolean := false; -- use barrel shifter for shift operations
|
-- Physical Memory Protection (PMP) --
|
-- Physical Memory Protection (PMP) --
|
PMP_USE : boolean := false; -- implement PMP?
|
PMP_USE : boolean := false; -- implement PMP?
|
PMP_NUM_REGIONS : natural := 4; -- number of regions (max 8)
|
PMP_NUM_REGIONS : natural := 4; -- number of regions (max 8)
|
PMP_GRANULARITY : natural := 14 -- minimal region granularity (1=8B, 2=16B, 3=32B, ...) default is 64k
|
PMP_GRANULARITY : natural := 14 -- minimal region granularity (1=8B, 2=16B, 3=32B, ...) default is 64k
|
);
|
);
|
| Line 454... |
Line 461... |
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_U : boolean := false; -- implement user mode extension?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_U : boolean := false; -- implement user mode extension?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zicsr : boolean := true; -- implement CSR system?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zicsr : boolean := true; -- implement CSR system?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zifencei : boolean := true; -- implement instruction stream sync.?
|
CPU_EXTENSION_RISCV_Zifencei : boolean := true; -- implement instruction stream sync.?
|
-- Extension Options --
|
-- Extension Options --
|
FAST_MUL_EN : boolean := false; -- use DSPs for M extension's multiplier
|
FAST_MUL_EN : boolean := false; -- use DSPs for M extension's multiplier
|
|
FAST_SHIFT_EN : boolean := false; -- use barrel shifter for shift operations
|
-- Physical Memory Protection (PMP) --
|
-- Physical Memory Protection (PMP) --
|
PMP_USE : boolean := false; -- implement PMP?
|
PMP_USE : boolean := false; -- implement PMP?
|
PMP_NUM_REGIONS : natural := 4; -- number of regions (max 8)
|
PMP_NUM_REGIONS : natural := 4; -- number of regions (max 8)
|
PMP_GRANULARITY : natural := 14; -- minimal region granularity (1=8B, 2=16B, 3=32B, ...) default is 64kB
|
PMP_GRANULARITY : natural := 14; -- minimal region granularity (1=8B, 2=16B, 3=32B, ...) default is 64kB
|
-- Internal Instruction memory --
|
-- Internal Instruction memory --
|
| Line 477... |
Line 485... |
IO_SPI_USE : boolean := true; -- implement serial peripheral interface (SPI)?
|
IO_SPI_USE : boolean := true; -- implement serial peripheral interface (SPI)?
|
IO_TWI_USE : boolean := true; -- implement two-wire interface (TWI)?
|
IO_TWI_USE : boolean := true; -- implement two-wire interface (TWI)?
|
IO_PWM_USE : boolean := true; -- implement pulse-width modulation unit (PWM)?
|
IO_PWM_USE : boolean := true; -- implement pulse-width modulation unit (PWM)?
|
IO_WDT_USE : boolean := true; -- implement watch dog timer (WDT)?
|
IO_WDT_USE : boolean := true; -- implement watch dog timer (WDT)?
|
IO_TRNG_USE : boolean := false; -- implement true random number generator (TRNG)?
|
IO_TRNG_USE : boolean := false; -- implement true random number generator (TRNG)?
|
IO_CFU_USE : boolean := false -- implement custom functions unit (CFU)?
|
IO_CFU0_USE : boolean := false; -- implement custom functions unit 0 (CFU0)?
|
|
IO_CFU1_USE : boolean := false -- implement custom functions unit 1 (CFU1)?
|
);
|
);
|
port (
|
port (
|
-- Global control --
|
-- Global control --
|
clk_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global clock, rising edge
|
clk_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global clock, rising edge
|
rstn_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global reset, low-active, async
|
rstn_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- global reset, low-active, async
|
| Line 513... |
Line 522... |
twi_sda_io : inout std_logic := 'H'; -- twi serial data line
|
twi_sda_io : inout std_logic := 'H'; -- twi serial data line
|
twi_scl_io : inout std_logic := 'H'; -- twi serial clock line
|
twi_scl_io : inout std_logic := 'H'; -- twi serial clock line
|
-- PWM (available if IO_PWM_USE = true) --
|
-- PWM (available if IO_PWM_USE = true) --
|
pwm_o : out std_ulogic_vector(03 downto 0); -- pwm channels
|
pwm_o : out std_ulogic_vector(03 downto 0); -- pwm channels
|
-- Interrupts --
|
-- Interrupts --
|
|
mtime_irq_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- machine timer interrupt, available if IO_MTIME_USE = false
|
msw_irq_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- machine software interrupt
|
msw_irq_i : in std_ulogic := '0'; -- machine software interrupt
|
mext_irq_i : in std_ulogic := '0' -- machine external interrupt
|
mext_irq_i : in std_ulogic := '0' -- machine external interrupt
|
);
|
);
|
end neorv32_top;
|
end neorv32_top;
|
```
|
```
|
| Line 602... |
Line 612... |
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make clean_all exe
|
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make clean_all exe
|
|
|
|
|
### Upload the Executable via the Bootloader
|
### Upload the Executable via the Bootloader
|
|
|
|
You can upload a generated executable directly from the command line using the makefile's `upload` target. Replace `/dev/ttyUSB0` with
|
|
the according serial port.
|
|
|
|
sw/exeample/blink_example$ make COM_PORT=/dev/ttyUSB0` upload
|
|
|
|
A more "secure" way is to use a dedicated terminal program. This allows to directly interact with the bootloader console.
|
Connect your FPGA board via UART to your computer and open the according port to interface with the NEORV32 bootloader. The bootloader
|
Connect your FPGA board via UART to your computer and open the according port to interface with the NEORV32 bootloader. The bootloader
|
uses the following default UART configuration:
|
uses the following default UART configuration:
|
|
|
* 19200 Baud
|
* 19200 Baud
|
* 8 data bits
|
* 8 data bits
|
| Line 673... |
Line 689... |
This project is released under the BSD 3-Clause license. No copyright infringement intended.
|
This project is released under the BSD 3-Clause license. No copyright infringement intended.
|
Other implied or used projects might have different licensing - see their documentation to get more information.
|
Other implied or used projects might have different licensing - see their documentation to get more information.
|
|
|
#### Citation
|
#### Citation
|
|
|
If you are using the NEORV32 Processor/CPU in some kind of publication, please cite it as follows:
|
If you are using the NEORV32 or some parts of the project in some kind of publication, please cite it as follows:
|
|
|
> S. Nolting, "The NEORV32 Processor/CPU", github.com/stnolting/neorv32
|
> S. Nolting, "The NEORV32 Processor", github.com/stnolting/neorv32
|
|
|
#### BSD 3-Clause License
|
#### BSD 3-Clause License
|
|
|
Copyright (c) 2020, Stephan Nolting. All rights reserved.
|
Copyright (c) 2020, Stephan Nolting. All rights reserved.
|
|
|
