| Line 23... |
Line 23... |
|
|
The NEORV32 Processor is a customizable microcontroller-like system on chip (SoC) that is based
|
The NEORV32 Processor is a customizable microcontroller-like system on chip (SoC) that is based
|
on the RISC-V-compliant NEORV32 CPU. The processor is intended as *ready-to-go* auxiliary processor within a larger SoC
|
on the RISC-V-compliant NEORV32 CPU. The processor is intended as *ready-to-go* auxiliary processor within a larger SoC
|
designs or as stand-alone custom microcontroller.
|
designs or as stand-alone custom microcontroller.
|
|
|
:label: The project’s change log is available in the [CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) file in the root directory of this repository.
|
:books: For detailed information take a look at the [NEORV32 data sheet (pdf)](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
To see the changes between releases visit the project's [release page](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases).
|
The doxygen-based documentation of the *software framework* is available online at [GitHub-pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html).
|
|
|
:books: The doxygen-based documentation of the software framework is available online at [GitHub-pages](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html).
|
:label: The project’s change log is available as [CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) in the root directory of this repository.
|
|
To see the changes between *stable* releases visit the project's [release page](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases).
|
|
|
:page_facing_up: For more detailed information take a look at the [NEORV32 data sheet (pdf)](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
:spiral_notepad: Check out the [project boards](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/projects) for a list of current ideas, ToDos, features being planned and work being in-progress.
|
|
|
|
:bulb: Feel free to open a [new issue](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/issues) or start a [new discussion](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/discussions)
|
|
if you have questions, comments, ideas or bug-fixes. Check out how to [contribute](#ContributeFeedbackQuestions).
|
|
|
|
|
### Key Features
|
### Key Features
|
|
|
* RISC-V 32-bit `rv32` [**NEORV32 CPU**](#NEORV32-CPU-Features), compliant to
|
* RISC-V 32-bit `rv32` [**NEORV32 CPU**](#NEORV32-CPU-Features), compliant to
|
* subset of the *Unprivileged ISA Specification* [(Version 2.2)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-privileged.pdf)
|
* subset of the *Unprivileged ISA Specification* [(Version 2.2)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)
|
* subset of the *Privileged Architecture Specification* [(Version 1.12-draft)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-spec.pdf)
|
* subset of the *Privileged Architecture Specification* [(Version 1.12-draft)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/docs/riscv-privileged.pdf)
|
* the [official RISC-V compliance tests](#Status) (*passing*)
|
* the [official RISC-V compliance tests](#Status) (*passing*)
|
* Configurable RISC-V-compliant CPU extensions
|
* Configurable RISC-V-compliant CPU extensions
|
* [`A`](#Atomic-memory-access-a-extension) - atomic memory access instructions (optional)
|
* [`A`](#A---Atomic-memory-access-extension) - atomic memory access instructions (optional)
|
* [`B`](#Bit-manipulation-instructions-B-extension) - Bit manipulation instructions (optional)
|
* [`B`](#B---Bit-manipulation-instructions-extension) - Bit manipulation instructions (optional)
|
* [`C`](#Compressed-instructions-C-extension) - compressed instructions (16-bit) (optional)
|
* [`C`](#C---Compressed-instructions-extension) - compressed instructions (16-bit) (optional)
|
* [`E`](#Embedded-CPU-version-E-extension) - embedded CPU (reduced register file size) (optional)
|
* [`E`](#E---Embedded-CPU-version-extension) - embedded CPU (reduced register file size) (optional)
|
* [`I`](#Integer-base-instruction-set-I-extension) - base integer instruction set (always enabled)
|
* [`I`](#I---Base-integer-instruction-set) - base integer instruction set (always enabled)
|
* [`M`](#Integer-multiplication-and-division-hardware-M-extension) - integer multiplication and division hardware (optional)
|
* [`M`](#M---Integer-multiplication-and-division-hardware-extension) - integer multiplication and division hardware (optional)
|
* [`U`](#Privileged-architecture---User-mode-U-extension) - less-privileged *user mode* (optional)
|
* [`U`](#U---Privileged-architecture---User-mode-extension) - less-privileged *user mode* (optional)
|
* [`X`](#NEORV32-specific-CPU-extensions-X-extension) - NEORV32-specific extensions (always enabled)
|
* [`X`](#X---NEORV32-specific-CPU-extensions) - NEORV32-specific extensions (always enabled)
|
* [`Zicsr`](#Privileged-architecture---CSR-access-Zicsr-extension) - control and status register access instructions (+ exception/irq system) (optional)
|
* [`Zicsr`](#Zicsr---Privileged-architecture---CSR-access-extension) - control and status register access instructions (+ exception/irq system) (optional)
|
* [`Zifencei`](#Privileged-architecture---Instruction-stream-synchronization-Zifencei-extension) - instruction stream synchronization (optional)
|
* [`Zifencei`](#Zifencei---Privileged-architecture---Instruction-stream-synchronization-extension) - instruction stream synchronization (optional)
|
* [`PMP`](#Privileged-architecture---Physical-memory-protection-PMP) - physical memory protection (optional)
|
* [`PMP`](#PMP---Privileged-architecture---Physical-memory-protection) - physical memory protection (optional)
|
* [`HPM`](#Privileged-architecture---Hardware-performance-monitors-HPM-extension) - hardware performance monitors (optional)
|
* [`HPM`](#HPM---Privileged-architecture---Hardware-performance-monitors) - hardware performance monitors (optional)
|
* Full-scale RISC-V microcontroller system / **SoC** [**NEORV32 Processor**](#NEORV32-Processor-Features) with optional submodules
|
* Full-scale RISC-V microcontroller system / **SoC** [**NEORV32 Processor**](#NEORV32-Processor-Features) with optional submodules
|
* optional embedded memories (instructions/data/bootloader, RAM/ROM) and caches
|
* optional embedded memories (instructions/data/bootloader, RAM/ROM) and caches
|
* timers (watch dog, RISC-V-compliant machine timer)
|
* timers (watch dog, RISC-V-compliant machine timer)
|
* serial interfaces (SPI, TWI, UARTs)
|
* serial interfaces (SPI, TWI, UARTs)
|
* general purpose IO and PWM channels
|
* general purpose IO and PWM channels
|
| Line 79... |
Line 83... |
|
|
* From zero to *hello_world*: Completely open source and documented.
|
* From zero to *hello_world*: Completely open source and documented.
|
* Plain VHDL without technology-specific parts like attributes, macros or primitives.
|
* Plain VHDL without technology-specific parts like attributes, macros or primitives.
|
* Easy to use – working out of the box.
|
* Easy to use – working out of the box.
|
* Clean synchronous design, no wacky combinatorial interfaces.
|
* Clean synchronous design, no wacky combinatorial interfaces.
|
* Be as small as possible – but with a reasonable size-performance tradeoff.
|
* Be as small as possible – but with a reasonable size-performance trade-off.
|
* Be as RISC-V-compliant as possible.
|
* Be as RISC-V-compliant as possible.
|
* The processor has to fit in a Lattice iCE40 UltraPlus 5k low-power FPGA running at 20+ MHz.
|
* The processor has to fit in a Lattice iCE40 UltraPlus 5k low-power FPGA running at 22+ MHz.
|
|
|
|
|
### Status
|
### Status
|
|
|
The processor is [synthesizable](#FPGA-Implementation-Results) (tested on *real hardware* using Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx Vivado and Lattice Radiant/Synplify Pro) and can successfully execute
|
The processor is [synthesizable](#FPGA-Implementation-Results) (tested on *real hardware* using Intel Quartus Prime, Xilinx Vivado and Lattice Radiant/Synplify Pro) and can successfully execute
|
| Line 101... |
Line 105... |
| [SW Framework Documentation (online @GH-pages)](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) | [](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) |
|
| [SW Framework Documentation (online @GH-pages)](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) | [](https://stnolting.github.io/neorv32/files.html) |
|
| [Pre-built toolchains](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Test+Toolchains%22) |
|
| [Pre-built toolchains](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/riscv-gcc-prebuilt/actions?query=workflow%3A%22Test+Toolchains%22) |
|
| [RISC-V compliance test](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/riscv-compliance/README.md) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22RISC-V+Compliance%22) |
|
| [RISC-V compliance test](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/riscv-compliance/README.md) | [](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/actions?query=workflow%3A%22RISC-V+Compliance%22) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### To-Do / Wish List / Help Wanted
|
|
|
|
* Use LaTeX for data sheet
|
|
* Further size and performance optimization
|
|
* Further expand associativity configuration of instruction cache (4x/8x set-associativity)?
|
|
* Add data cache?
|
|
* Burst mode for the external memory/bus interface?
|
|
* RISC-V `F` (using [`Zfinx`](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-zfinx/blob/master/Zfinx_spec.adoc)?) CPU extension (single-precision floating point)
|
|
* RISC-V `K` CPU extension: [Crypto](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-crypto)
|
|
* Add template (HW module + SW intrinsics skeleton) for custom instructions?
|
|
* Implement further RISC-V CPU extensions?
|
|
* More support for FreeRTOS?
|
|
* Port additional RTOSs (like [Zephyr](https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr) or [RIOT](https://www.riot-os.org))?
|
|
* Add debugger ([RISC-V debug spec](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-debug-spec))?
|
|
* ...
|
|
* [Ideas?](#ContributeFeedbackQuestions)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Features
|
## Features
|
|
|
The full-blown data sheet of the NEORV32 Processor and CPU is available as pdf file:
|
The full-blown data sheet of the NEORV32 Processor and CPU is available as pdf file:
|
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
|
|
| Line 138... |
Line 122... |
|
|
* processor-internal data and instruction memories (**DMEM** / **IMEM**) & cache (**iCACHE**)
|
* processor-internal data and instruction memories (**DMEM** / **IMEM**) & cache (**iCACHE**)
|
* bootloader (**BOOTLDROM**) with UART console and automatic application boot from SPI flash option
|
* bootloader (**BOOTLDROM**) with UART console and automatic application boot from SPI flash option
|
* machine system timer (**MTIME**), RISC-V-compliant
|
* machine system timer (**MTIME**), RISC-V-compliant
|
* watchdog timer (**WDT**)
|
* watchdog timer (**WDT**)
|
* two independent universal asynchronous receiver and transmitter (**UART0** & **UART1**) with fast simulation output option
|
* two independent universal asynchronous receivers and transmitters (**UART0** & **UART1**) with optional hardware flow control (RTS/CTS)
|
* 8/16/24/32-bit serial peripheral interface controller (**SPI**) with 8 dedicated chip select lines
|
* 8/16/24/32-bit serial peripheral interface controller (**SPI**) with 8 dedicated chip select lines
|
* two wire serial interface controller (**TWI**), with optional clock-stretching, compatible to the I²C standard
|
* two wire serial interface controller (**TWI**), with optional clock-stretching, compatible to the I²C standard
|
* general purpose parallel IO port (**GPIO**), 32xOut & 32xIn, with pin-change interrupt
|
* general purpose parallel IO port (**GPIO**), 32xOut & 32xIn, with pin-change interrupt
|
* 32-bit external bus interface, Wishbone b4 compliant (**WISHBONE**), *standard* or *pipelined* handshake/transactions mode
|
* 32-bit external bus interface, Wishbone b4 compliant (**WISHBONE**)
|
* wrapper for **AXI4-Lite Master Interface** (see [AXI Connectivity](#AXI4-Connectivity))
|
* wrapper for **AXI4-Lite Master Interface** (see [AXI Connectivity](#AXI4-Connectivity))
|
* PWM controller with 4 channels and 8-bit duty cycle resolution (**PWM**)
|
* PWM controller with 4 channels and 8-bit duty cycle resolution (**PWM**)
|
* ring-oscillator-based true random number generator (**TRNG**)
|
* ring-oscillator-based true random number generator (**TRNG**)
|
* custom functions subsystem (**CFS**) for tightly-coupled custom co-processor extensions
|
* custom functions subsystem (**CFS**) for tightly-coupled custom co-processor extensions
|
* numerically-controlled oscillator (**NCO**) with three independent channels
|
* numerically-controlled oscillator (**NCO**) with three independent channels
|
* system configuration information memory to check hardware configuration by software (**SYSINFO**, mandatory - not *optional*)
|
* system configuration information memory to check hardware configuration by software (**SYSINFO**)
|
|
|
|
|
### NEORV32 CPU Features
|
### NEORV32 CPU Features
|
|
|
The NEORV32 CPU is **compliant** to the
|
The NEORV32 CPU is **compliant** to the
|
| Line 174... |
Line 158... |
* All reserved or unimplemented instructions will raise an illegal instruction exception
|
* All reserved or unimplemented instructions will raise an illegal instruction exception
|
* Privilege levels: `machine` mode, `user` mode (if enabled via `U` extension)
|
* Privilege levels: `machine` mode, `user` mode (if enabled via `U` extension)
|
* Official [RISC-V open-source architecture ID](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md)
|
* Official [RISC-V open-source architecture ID](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md)
|
|
|
|
|
#### Atomic memory access (`A` extension)
|
#### `A` - Atomic memory access extension
|
|
|
* Supported instructions: `LR.W` (load-reservate) `SC.W` (store-conditional)
|
* Supported instructions: `LR.W` (load-reservate) `SC.W` (store-conditional)
|
|
|
|
|
#### Bit manipulation instructions (`B` extension)
|
#### `B` - Bit manipulation instructions extension
|
|
|
* :warning: Extension is not officially ratified yet by the RISC-V foundation!
|
* :warning: Extension is not officially ratified yet by the RISC-V foundation!
|
* Implies `Zbb` extension (base bit manipulation instruction set)
|
* Implies `Zbb` & `Zbs` sub-extensions (the remaining `B` sub-extensions are not supported yet)
|
* Compatible to [v0.94-draft](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/bitmanip-draft.pdf) of the bit manipulation spec
|
* Compatible to [v0.94-draft](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/bitmanip-draft.pdf) of the bit manipulation spec
|
* Support via intrisc library (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation))
|
* Support via intrisc library (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation))
|
* Only the `Zbb` base instructions subset is supported yet
|
* `Zbb` Base instruction set: `CLZ` `CTZ` `CPOP` `SEXT.B` `SEXT.H` `MIN[U]` `MAX[U]` `ANDN` `ORN` `XNOR` `ROL` `ROR[I]` `zext`(*pseudo-instruction* for `PACK rd, rs, zero`) `rev8`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GREVI rd, rs, -8`) `orc.b`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GORCI rd, rs, 7`)
|
* Supported instructions: `CLZ` `CTZ` `CPOP` `SEXT.B` `SEXT.H` `MIN[U]` `MAX[U]` `ANDN` `ORN` `XNOR` `ROL` `ROR` `RORI` `zext`(*pseudo-instruction* for `PACK rd, rs, zero`) `rev8`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GREVI rd, rs, -8`) `orc.b`(*pseudo-instruction* for `GORCI rd, rs, 7`)
|
* `Zbs` Single-bit instructions: `SBSET[I]` `SBCLR[I]` `SBINV[I]` `SBEXT[I]`
|
|
|
|
|
#### Compressed instructions (`C` extension)
|
#### `C` - Compressed instructions extension
|
|
|
* ALU instructions: `C.ADDI4SPN` `C.ADDI` `C.ADD` `C.ADDI16SP` `C.LI` `C.LUI` `C.SLLI` `C.SRLI` `C.SRAI` `C.ANDI` `C.SUB` `C.XOR` `C.OR` `C.AND` `C.MV` `C.NOP`
|
* ALU instructions: `C.ADDI4SPN` `C.ADD[I]` `C.ADDI16SP` `C.LI` `C.LUI` `C.SLLI` `C.SRLI` `C.SRAI` `C.ANDI` `C.SUB` `C.XOR` `C.OR` `C.AND` `C.MV` `C.NOP`
|
* Jump and branch instructions: `C.J` `C.JAL` `C.JR` `C.JALR` `C.BEQZ` `C.BNEZ`
|
* Jump and branch instructions: `C.J` `C.JAL` `C.JR` `C.JALR` `C.BEQZ` `C.BNEZ`
|
* Memory instructions: `C.LW` `C.SW` `C.LWSP` `C.SWSP`
|
* Memory instructions: `C.LW` `C.SW` `C.LWSP` `C.SWSP`
|
* System instructions: `C.EBREAK` (only with `Zicsr` extension)
|
* System instructions: `C.EBREAK` (only with `Zicsr` extension)
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
|
|
#### Embedded CPU version (`E` extension)
|
#### `E` - Embedded CPU version extension
|
|
|
* Reduced register file (only the 16 lowest registers)
|
* Reduced register file (only the 16 lowest registers)
|
|
|
|
|
#### Integer base instruction set (`I` extension)
|
#### `I` - Base integer instruction set
|
|
|
* ALU instructions: `LUI` `AUIPC` `ADDI` `SLTI` `SLTIU` `XORI` `ORI` `ANDI` `SLLI` `SRLI` `SRAI` `ADD` `SUB` `SLL` `SLT` `SLTU` `XOR` `SRL` `SRA` `OR` `AND`
|
* ALU instructions: `LUI` `AUIPC` `ADD[I]` `SLT[I][U]` `XOR[I]` `OR[I]` `AND[I]` `SLL[I]` `SRL[I]` `SRA[I]` `SUB`
|
* Jump and branch instructions: `JAL` `JALR` `BEQ` `BNE` `BLT` `BGE` `BLTU` `BGEU`
|
* Jump and branch instructions: `JAL` `JALR` `BEQ` `BNE` `BLT` `BGE` `BLTU` `BGEU`
|
* Memory instructions: `LB` `LH` `LW` `LBU` `LHU` `SB` `SH` `SW`
|
* Memory instructions: `LB` `LH` `LW` `LBU` `LHU` `SB` `SH` `SW`
|
* System instructions: `ECALL` `EBREAK` `FENCE`
|
* System instructions: `ECALL` `EBREAK` `FENCE`
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
|
|
|
|
#### Integer multiplication and division hardware (`M` extension)
|
#### `M` - Integer multiplication and division hardware extension
|
|
|
* Multiplication instructions: `MUL` `MULH` `MULHSU` `MULHU`
|
* Multiplication instructions: `MUL` `MULH` `MULHSU` `MULHU`
|
* Division instructions: `DIV` `DIVU` `REM` `REMU`
|
* Division instructions: `DIV` `DIVU` `REM` `REMU`
|
* By default, the multiplier and divider cores use an iterative bit-serial processing scheme
|
* By default, the multiplier and divider cores use an iterative bit-serial processing scheme
|
* Multiplications can be mapped to DSPs via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic to increase performance
|
* Multiplications can be mapped to DSPs via the `FAST_MUL_EN` generic to increase performance
|
|
|
|
|
#### Privileged architecture - User mode (`U` extension)
|
#### `U` - Privileged architecture - User mode extension
|
|
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Privilege levels: `M` (machine mode) + less-privileged `U` (user mode)
|
* Privilege levels: `M` (machine mode) + less-privileged `U` (user mode)
|
|
|
|
|
#### NEORV32-specific CPU extensions (`X` extension)
|
#### `X` - NEORV32-specific CPU extensions
|
|
|
* The NEORV32-specific extensions are always enabled and are indicated via the `X` bit set in the `misa` CSR.
|
* The NEORV32-specific extensions are always enabled and are indicated via the `X` bit set in the `misa` CSR.
|
* 16 *fast interrupt* request channels with according control/status bits in `mie` and `mip` and custom exception codes in `mcause`
|
* 16 *fast interrupt* request channels with according control/status bits in `mie` and `mip` and custom exception codes in `mcause`
|
* `mzext` CSR to check for implemented `Z*` CPU extensions (like `Zifencei`)
|
* `mzext` CSR to check for implemented `Z*` CPU extensions (like `Zifencei`)
|
* All undefined/umimplemented/malformed/illegal instructions do raise an illegal instruction exception
|
* All undefined/umimplemented/malformed/illegal instructions do raise an illegal instruction exception
|
|
|
|
|
#### Privileged architecture - CSR access (`Zicsr` extension)
|
#### `Zicsr` - Privileged architecture - CSR access extension
|
|
|
* Privilege levels: `M-mode` (Machine mode)
|
* Privilege levels: `M-mode` (Machine mode)
|
* CSR access instructions: `CSRRW` `CSRRS` `CSRRC` `CSRRWI` `CSRRSI` `CSRRCI`
|
* CSR access instructions: `CSRRW[I]` `CSRRS[I]` `CSRRC[I]`
|
* System instructions: `MRET` `WFI`
|
* System instructions: `MRET` `WFI`
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
* Pseudo-instructions are not listed
|
* Counter CSRs: `[m]cycle[h]` `[m]instret[m]` `time[h]` `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31, configurable) `mcounteren` `mcountinhibit` `mhpmevent*`(3..31, configurable)
|
* Counter CSRs: `[m]cycle[h]` `[m]instret[m]` `time[h]` `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31, configurable) `mcounteren` `mcountinhibit` `mhpmevent*`(3..31, configurable)
|
* Machine CSRs: `mstatus[h]` `misa`(read-only!) `mie` `mtvec` `mscratch` `mepc` `mcause` `mtval` `mip` `mvendorid` [`marchid`](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md) `mimpid` `mhartid` `mzext`(custom)
|
* Machine CSRs: `mstatus[h]` `misa`(read-only!) `mie` `mtvec` `mscratch` `mepc` `mcause` `mtval` `mip` `mvendorid` [`marchid`](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-isa-manual/blob/master/marchid.md) `mimpid` `mhartid` `mzext`(custom)
|
* Supported exceptions and interrupts:
|
* Supported (sync.) exceptions (all RISC-V-compliant):
|
* Misaligned instruction address
|
* Misaligned instruction address
|
* Instruction access fault (via unacknowledged bus access after timeout)
|
* Instruction access fault (via timeout/error after unacknowledged bus access)
|
* Illegal instruction
|
* Illegal instruction
|
* Breakpoint (via `ebreak` instruction)
|
* Breakpoint (via `ebreak` instruction)
|
* Load address misaligned
|
* Load address misaligned
|
* Load access fault (via unacknowledged bus access after timeout)
|
* Load access fault (via timeout/error after unacknowledged bus access)
|
* Store address misaligned
|
* Store address misaligned
|
* Store access fault (via unacknowledged bus access after timeout)
|
* Store access fault (via unacknowledged bus access after timeout)
|
* Environment call from U-mode (via `ecall` instruction in user mode)
|
* Environment call from U-mode (via `ecall` instruction in user mode)
|
* Environment call from M-mode (via `ecall` instruction in machine mode)
|
* Environment call from M-mode (via `ecall` instruction in machine mode)
|
* Machine timer interrupt `mti` (via processor's MTIME unit / external signal)
|
* Supported (async.) exceptions / interrupts:
|
* Machine software interrupt `msi` (via external signal)
|
* Machine timer interrupt `mti` (via processor's MTIME unit / external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
* Machine external interrupt `mei` (via external signal)
|
* Machine software interrupt `msi` (via external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
* Eight fast interrupt requests (custom extension)
|
* Machine external interrupt `mei` (via external signal), RISC-V-compliant
|
|
* 16 fast interrupt requests (custom extension), 6+1 available for custom usage
|
|
|
|
|
#### Privileged architecture - Instruction stream synchronization (`Zifencei` extension)
|
#### `Zifencei` - Privileged architecture - Instruction stream synchronization extension
|
|
|
* System instructions: `FENCE.I` (among others, used to clear and reload instruction cache)
|
* System instructions: `FENCE.I` (among others, used to clear and reload instruction cache)
|
|
|
|
|
#### Privileged architecture - Physical memory protection (`PMP`)
|
#### `PMP` - Privileged architecture - Physical memory protection
|
|
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Configurable number of regions (0..63)
|
* Configurable number of regions (0..63)
|
* Additional machine CSRs: `pmpcfg*`(0..15) `pmpaddr*`(0..63)
|
* Additional machine CSRs: `pmpcfg*`(0..15) `pmpaddr*`(0..63)
|
|
|
|
|
#### Privileged architecture - Hardware performance monitors (`HPM` extension)
|
#### `HPM` - Privileged architecture - Hardware performance monitors
|
|
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Requires `Zicsr` extension
|
* Configurable number of counters (0..29)
|
* Configurable number of counters (0..29)
|
* Additional machine CSRs: `mhpmevent*`(3..31) `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31)
|
* Additional machine CSRs: `mhpmevent*`(3..31) `[m]hpmcounter*[h]`(3..31)
|
|
|
| Line 284... |
Line 269... |
* CPU and Processor are BIG-ENDIAN, but this should be no problem as the external memory bus interface provides big- and little-endian configurations
|
* CPU and Processor are BIG-ENDIAN, but this should be no problem as the external memory bus interface provides big- and little-endian configurations
|
* `misa` CSR is read-only - no dynamic enabling/disabling of synthesized CPU extensions during runtime; for compatibility: write accesses (in m-mode) are ignored and do not cause an exception
|
* `misa` CSR is read-only - no dynamic enabling/disabling of synthesized CPU extensions during runtime; for compatibility: write accesses (in m-mode) are ignored and do not cause an exception
|
* The physical memory protection (**PMP**) only supports `NAPOT` mode yet and a minimal granularity of 8 bytes
|
* The physical memory protection (**PMP**) only supports `NAPOT` mode yet and a minimal granularity of 8 bytes
|
* The `A` extension only implements `lr.w` and `sc.w` instructions yet. However, these instructions are sufficient to emulate all further AMO operations
|
* The `A` extension only implements `lr.w` and `sc.w` instructions yet. However, these instructions are sufficient to emulate all further AMO operations
|
* The `mcause` trap code `0x80000000` (originally reserved in the RISC-V specs) is used to indicate a hardware reset (as "non-maskable interrupt")
|
* The `mcause` trap code `0x80000000` (originally reserved in the RISC-V specs) is used to indicate a hardware reset (as "non-maskable interrupt")
|
* The bit manipulation extension is not yet officially ratified, but is expected to stay unchanged. There is no software support in the upstream GCC RISC-V port yet. However, an intrinsic library is provided to utilize the provided bit manipulation extension from C-language code (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation)). NEORV32's `B`/`Zbb` extension is compliant to spec. version "0.94-draft".
|
* The bit manipulation extension is not yet officially ratified, but is expected to stay unchanged. There is no software support in the upstream GCC RISC-V port yet. However, an intrinsic library is provided to utilize the provided bit manipulation extension from C-language code (see [`sw/example/bit_manipulation`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/sw/example/bit_manipulation)). NEORV32's `B` extension is compliant to spec. version "0.94-draft".
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## FPGA Implementation Results
|
## FPGA Implementation Results
|
|
|
| Line 431... |
Line 416... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Top Entities
|
## Top Entities
|
|
|
The top entity of the **NEORV32 Processor** (SoC) is [`rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd).
|
The top entity of the **NEORV32 Processor** (SoC) is [`rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd),
|
|
which provides a Wishbone b4-compatoible bus interface.
|
|
|
All signals of the top entity are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively
|
:information_source: It is recommended to use the processor setup even if you want to **use the CPU in stand-alone mode**. Simply disable all the processor-internal
|
(except for the processor's TWI signals, which are of type *std_logic*). Leave all unused output ports unconnected (`open`) and tie all unused
|
modules via the generics and you will get a "CPU wrapper" that already provides a minimal CPU environment and an external memory interface (like AXI4).
|
input ports to zero (`'0'` or `(others => '0')`, respectively).
|
This setup also allows to further use the default bootloader and software framework. From this base you can start building your own processor system.
|
|
|
Use the top's generics to configure the system according to your needs. Each generic is initilized with the default configuration.
|
Use the top's generics to configure the system according to your needs. Each generic is initilized with the default configuration.
|
Detailed information regarding the interface signals and configuration generics can be found in
|
Detailed information regarding the interface signals and configuration generics can be found in
|
the [:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf).
|
the [:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf) (pdf).
|
|
|
|
All signals of the top entity are of type *std_ulogic* or *std_ulogic_vector*, respectively
|
|
(except for the processor's TWI signals, which are of type *std_logic*). Leave all unused output ports unconnected and tie all unused
|
|
input ports to zero.
|
|
|
### Using the CPU in Stand-Alone Mode
|
**Alternative top entities**, like the simplified ["hello world" test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project) or CPU/Processor
|
|
|
If you *do not* want to use the NEORV32 processor setup, you can also use the CPU in stand-alone mode and build your own system around it.
|
|
The top entity of the stand-alone **NEORV32 CPU** is [`rtl/core/neorv32_cpu.vhd`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_cpu.vhd).
|
|
Note that the CPU uses a proprietary interface for accessing data and instruction memory. More information can be found in the
|
|
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf).
|
|
|
|
:information_source: It is recommended to use the processor setup even if you only want to use the CPU. Simply disable all the processor-internal modules via the generics
|
|
and you will get a "CPU wrapper" that already provides a minimal CPU environment and an external memory interface (like AXI4). This setup also allows to further use the default
|
|
bootloader and software framework. From this base you can start building your own processor system.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### Alternative Top Entities
|
|
|
|
*Alternative top entities*, like the simplified ["hello world" test setup](#Create-a-new-Hardware-Project) or CPU/Processor
|
|
wrappers with resolved port signal types (i.e. *std_logic*), can be found in [`rtl/top_templates`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates).
|
wrappers with resolved port signal types (i.e. *std_logic*), can be found in [`rtl/top_templates`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates).
|
|
|
|
|
### AXI4 Connectivity
|
### AXI4 Connectivity
|
|
|
| Line 488... |
Line 463... |
This overview is just a short excerpt from the *Let's Get It Started* section of the NEORV32 documentary:
|
This overview is just a short excerpt from the *Let's Get It Started* section of the NEORV32 documentary:
|
|
|
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf)
|
[:page_facing_up: NEORV32 data sheet](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stnolting/neorv32/master/docs/NEORV32.pdf)
|
|
|
|
|
### 1. Get Toolchain
|
### 1. Get the Toolchain
|
|
|
At first you need a **RISC-V GCC toolchain**. You can either [download the sources](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain)
|
At first you need a **RISC-V GCC toolchain**. You can either [download the sources](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain)
|
and build the toolchain by yourself, or you can download a prebuilt one and install it.
|
and build the toolchain by yourself, or you can download a prebuilt one and install it.
|
|
|
To build the toolchain by yourself, follow the official [build instructions](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain).
|
To build the toolchain by yourself, follow the official [build instructions](https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain).
|
| Line 513... |
Line 488... |
`sw/example/blink_led` and running:
|
`sw/example/blink_led` and running:
|
|
|
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make check
|
neorv32/sw/example/blink_led$ make check
|
|
|
|
|
### 2. Dowload the NEORV32 Project
|
### 2. Download the NEORV32 Project
|
|
|
Get the sources of the NEORV32 Processor project. The simplest way is using `git clone` (suggested for easy project updates via `git pull`):
|
Get the sources of the NEORV32 Processor project. The simplest way is using `git clone` (suggested for easy project updates via `git pull`):
|
|
|
$ git clone https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32.git
|
$ git clone https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32.git
|
|
|
Alternatively, you can either download a specific [release](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases) or get the most recent version
|
Alternatively, you can either download a specific [release](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/releases) or get the most recent version
|
of this project as [`*.zip` file](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/archive/master.zip).
|
of this project as [`*.zip` file](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/archive/master.zip).
|
|
|
|
|
### 3. Create a new Hardware Project
|
### 3. Create a new FPGA Project
|
|
|
Create a new project with your FPGA design tool of choice. Add all the `*.vhd` files from the [`rtl/core`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl)
|
Create a new project with your FPGA design tool of choice. Add all the `*.vhd` files from the [`rtl/core`](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl)
|
folder to this project. Make sure to add these files to a **new design library** called `neorv32`.
|
folder to this project. Make sure to add these files to a **new design library** called `neorv32`.
|
|
|
You can either instantiate the [processor's top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) or one of its
|
You can either instantiate the [processor's top entity](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/core/neorv32_top.vhd) or one of its
|
[wrappers](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates) in your own project. If you just want to try out the processor,
|
[wrappers](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates) in your own project. If you just want to try thing out,
|
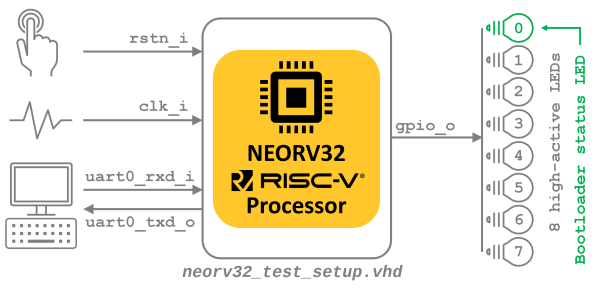
you can use the simple [test setup](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates/neorv32_test_setup.vhd) as top entity.
|
you can use the simple [**test setup** (`rtl/top_templates/neorv32_test_setup.vhd`)](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/blob/master/rtl/top_templates/neorv32_test_setup.vhd) as top entity.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
This test setup instantiates the processor and implements most of the peripherals and some ISA extensions. Only the UART0 lines, clock, reset and some GPIO output signals are
|
This test setup instantiates the processor and implements most of the peripherals and some ISA extensions. Only the UART0 communications lines, clock, reset and some
|
propagated as actual entity signals. Basically, it is a FPGA "hello world" example:
|
GPIO output signals are propagated as actual top entity interface signals. Basically, it is a FPGA version of a "hello world" example:
|
|
|
```vhdl
|
```vhdl
|
entity neorv32_test_setup is
|
entity neorv32_test_setup is
|
port (
|
port (
|
-- Global control --
|
-- Global control --
|
| Line 579... |
Line 554... |
* 1 stop bit
|
* 1 stop bit
|
* No parity bits
|
* No parity bits
|
* No transmission / flow control protocol (raw bytes only)
|
* No transmission / flow control protocol (raw bytes only)
|
* Newline on `\r\n` (carriage return & newline) - also for sent data
|
* Newline on `\r\n` (carriage return & newline) - also for sent data
|
|
|
Use the bootloader console to upload the `neorv32_exe.bin` executable gerated during application compiling and run your application.
|
Use the bootloader console to upload the `neorv32_exe.bin` executable gerated during application compiling and *run* your application.
|
|
|
```
|
```
|
<< NEORV32 Bootloader >>
|
<< NEORV32 Bootloader >>
|
|
|
BLDV: Nov 7 2020
|
BLDV: Nov 7 2020
|
| Line 617... |
Line 592... |
|
|
|
|
|
|
## Contribute/Feedback/Questions
|
## Contribute/Feedback/Questions
|
|
|
I'm always thankful for help! So if you have any questions, bug reports, ideas or if you want to give some kind of feedback, feel free
|
I'm always thankful for help! So if you have any questions, bug reports, ideas or if you want to give any kind of feedback, feel free
|
to [:bulb: open a new issue](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/issues), start a new [:sparkles: discussion on GitHub](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/discussions)
|
to [open a new issue](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/issues), start a new [discussion on GitHub](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/discussions)
|
or directly [:e-mail: drop me a line](mailto:stnolting@gmail.com).
|
or directly [drop me a line](mailto:stnolting@gmail.com).
|
|
|
If you'd like to directly contribute to this repository:
|
Here is a simple guide line if you'd like to contribute to this repository:
|
|
|
0. :star: this repository ;)
|
0. :star: this repository :wink:
|
1. Check out the project's [code of conduct](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md)
|
1. Check out the project's [code of conduct](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/tree/master/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md)
|
2. [Fork](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/fork) this repository and clone the fork
|
2. [Fork](https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32/fork) this repository and clone the fork
|
3. Create a feature branch in your fork: `git checkout -b awesome_new_feature_branch`
|
3. Create a feature branch in your fork: `git checkout -b awesome_new_feature_branch`
|
4. Create a new remote for the upstream repo: `git remote add upstream https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32`
|
4. Create a new remote for the upstream repo: `git remote add upstream https://github.com/stnolting/neorv32`
|
5. Commit your modifications: `git commit -m "Awesome new feature!"`
|
5. Commit your modifications: `git commit -m "Awesome new feature!"`
|
| Line 640... |
Line 615... |
This project is released under the BSD 3-Clause license. No copyright infringement intended.
|
This project is released under the BSD 3-Clause license. No copyright infringement intended.
|
Other implied or used projects might have different licensing - see their documentation to get more information.
|
Other implied or used projects might have different licensing - see their documentation to get more information.
|
|
|
#### Citing
|
#### Citing
|
|
|
If you are using the NEORV32 or some parts of the project in some kind of publication, please cite it as follows:
|
If you are using the NEORV32 or parts of the project in some kind of publication, please cite it as follows:
|
|
|
> S. Nolting, "The NEORV32 Processor", github.com/stnolting/neorv32
|
> S. Nolting, "The NEORV32 RISC-V Processor", github.com/stnolting/neorv32
|
|
|
#### BSD 3-Clause License
|
#### BSD 3-Clause License
|
|
|
Copyright (c) 2021, Stephan Nolting. All rights reserved.
|
Copyright (c) 2021, Stephan Nolting. All rights reserved.
|
|
|
